- Nobel Prize winners by name (S through U)
-
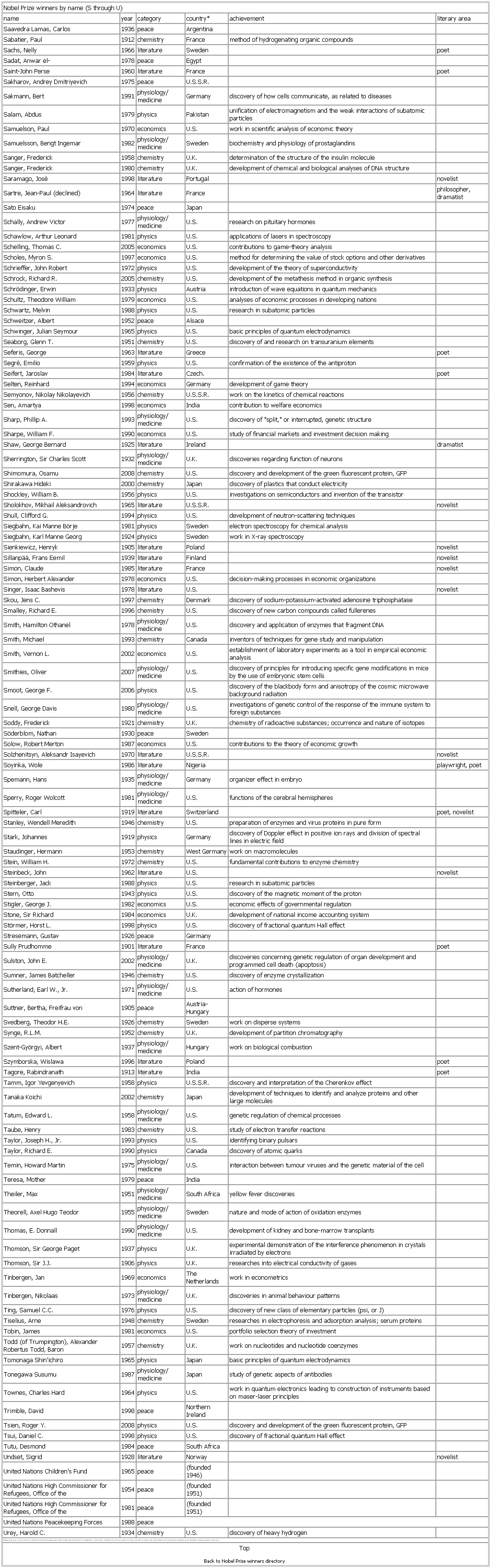
▪ TableNobel Prize winners by name (S through U)name year category country* achievement literary areaSaavedra Lamas, Carlos 1936 peace ArgentinaSabatier, Paul 1912 chemistry France method of hydrogenating organic compoundsSachs, Nelly 1966 literature Sweden poetSadat, Anwar el- (Sādāt, Anwar el-) 1978 peace EgyptSaint-John Perse 1960 literature France poetSakharov, Andrey Dmitriyevich 1975 peace U.S.S.R.Sakmann, Bert 1991 physiology/medicine Germany discovery of how cells communicate, as related to diseasesSalam, Abdus 1979 physics Pakistan unification of electromagnetism and the weak interactions of subatomic particlesSamuelson, Paul 1970 economics U.S. work in scientific analysis of economic theorySamuelsson, Bengt Ingemar 1982 physiology/medicine Sweden biochemistry and physiology of prostaglandinsSanger, Frederick 1958 chemistry U.K. determination of the structure of the insulin moleculeSanger, Frederick 1980 chemistry U.K. development of chemical and biological analyses of DNA structureSaramago, José 1998 literature Portugal novelistSartre, Jean-Paul (declined) 1964 literature France philosopher, dramatistSato Eisaku (Satō Eisaku) 1974 peace JapanSchally, Andrew Victor (Schally, Andrew V.) 1977 physiology/medicine U.S. research on pituitary hormonesSchawlow, Arthur Leonard (Schawlow, Arthur L.) 1981 physics U.S. applications of lasers in spectroscopySchelling, Thomas C. 2005 economics U.S. contributions to game-theory analysisScholes, Myron S. 1997 economics U.S. method for determining the value of stock options and other derivativesSchrieffer, John Robert 1972 physics U.S. development of the theory of superconductivitySchrock, Richard R. 2005 chemistry U.S. development of the metathesis method in organic synthesisSchrödinger, Erwin 1933 physics Austria introduction of wave equations in quantum mechanicsSchultz, Theodore William 1979 economics U.S. analyses of economic processes in developing nationsSchwartz, Melvin 1988 physics U.S. research in subatomic particlesSchweitzer, Albert 1952 peace AlsaceSchwinger, Julian Seymour 1965 physics U.S. basic principles of quantum electrodynamicsSeaborg, Glenn T. 1951 chemistry U.S. discovery of and research on transuranium elementsSeferis, George 1963 literature Greece poetSegrè, Emilio 1959 physics U.S. confirmation of the existence of the antiprotonSeifert, Jaroslav 1984 literature Czech. poetSelten, Reinhard 1994 economics Germany development of game theorySemyonov, Nikolay Nikolayevich 1956 chemistry U.S.S.R. work on the kinetics of chemical reactionsSen, Amartya 1998 economics India contribution to welfare economicsSharp, Phillip A. 1993 physiology/medicine U.S. discovery of "split," or interrupted, genetic structureSharpe, William F. 1990 economics U.S. study of financial markets and investment decision makingShaw, George Bernard 1925 literature Ireland dramatistSherrington, Sir Charles Scott 1932 physiology/ medicine U.K. discoveries regarding function of neuronsShimomura, Osamu 2008 chemistry U.S. discovery and development of the green fluorescent protein, GFPShirakawa Hideki 2000 chemistry Japan discovery of plastics that conduct electricityShockley, William B. 1956 physics U.S. investigations on semiconductors and invention of the transistorSholokhov, Mikhail Aleksandrovich 1965 literature U.S.S.R. novelistShull, Clifford G. 1994 physics U.S. development of neutron-scattering techniquesSiegbahn, Kai Manne Börje 1981 physics Sweden electron spectroscopy for chemical analysisSiegbahn, Karl Manne Georg 1924 physics Sweden work in X-ray spectroscopySienkiewicz, Henryk 1905 literature Poland novelistSillanpää, Frans Eemil 1939 literature Finland novelistSimon, Claude 1985 literature France novelistSimon, Herbert Alexander (Simon, Herbert A.) 1978 economics U.S. decision-making processes in economic organizationsSinger, Isaac Bashevis 1978 literature U.S. novelistSkou, Jens C. 1997 chemistry Denmark discovery of sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphataseSmalley, Richard E. 1996 chemistry U.S. discovery of new carbon compounds called fullerenesSmith, Hamilton Othanel 1978 physiology/medicine U.S. discovery and application of enzymes that fragment DNASmith, Michael 1993 chemistry Canada inventors of techniques for gene study and manipulationSmith, Vernon L. 2002 economics U.S. establishment of laboratory experiments as a tool in empirical economic analysisSmithies, Oliver 2007 physiology/medicine U.S. discovery of principles for introducing specific gene modifications in mice by the use of embryonic stem cellsSmoot, George F. 2006 physics U.S. discovery of the blackbody form and anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background radiationSnell, George Davis 1980 physiology/medicine U.S. investigations of genetic control of the response of the immune system to foreign substancesSoddy, Frederick 1921 chemistry U.K. chemistry of radioactive substances; occurrence and nature of isotopesSöderblom, Nathan 1930 peace SwedenSolow, Robert Merton (Solow, Robert M.) 1987 economics U.S. contributions to the theory of economic growthSolzhenitsyn, Aleksandr Isayevich 1970 literature U.S.S.R. novelistSoyinka, Wole 1986 literature Nigeria playwright, poetSpemann, Hans 1935 physiology/medicine Germany organizer effect in embryoSperry, Roger Wolcott 1981 physiology/medicine U.S. functions of the cerebral hemispheresSpitteler, Carl 1919 literature Switzerland poet, novelistStanley, Wendell Meredith 1946 chemistry U.S. preparation of enzymes and virus proteins in pure formStark, Johannes 1919 physics Germany discovery of Doppler effect in positive ion rays and division of spectral lines in electric fieldStaudinger, Hermann 1953 chemistry West Germany work on macromoleculesStein, William H. 1972 chemistry U.S. fundamental contributions to enzyme chemistrySteinbeck, John 1962 literature U.S. novelistSteinberger, Jack 1988 physics U.S. research in subatomic particlesStern, Otto 1943 physics U.S. discovery of the magnetic moment of the protonStigler, George J. 1982 economics U.S. economic effects of governmental regulationStone, Sir Richard 1984 economics U.K. development of national income accounting systemStörmer, Horst L. 1998 physics U.S. discovery of fractional quantum Hall effectStresemann, Gustav 1926 peace GermanySully Prudhomme 1901 literature France poetSulston, John E. 2002 physiology/medicine U.K. discoveries concerning genetic regulation of organ development and programmed cell death (apoptosis)Sumner, James Batcheller 1946 chemistry U.S. discovery of enzyme crystallizationSutherland, Earl W., Jr. 1971 physiology/medicine U.S. action of hormonesSuttner, Bertha, Freifrau von 1905 peace Austria- HungarySvedberg, Theodor H.E. 1926 chemistry Sweden work on disperse systemsSynge, R.L.M. 1952 chemistry U.K. development of partition chromatographySzent-Györgyi, Albert 1937 physiology/medicine Hungary work on biological combustionSzymborska, Wislawa (Szymborska, Wisława) 1996 literature Poland poetTagore, Rabindranath 1913 literature India poetTamm, Igor Yevgenyevich 1958 physics U.S.S.R. discovery and interpretation of the Cherenkov effectTanaka Koichi 2002 chemistry Japan development of techniques to identify and analyze proteins and other large moleculesTatum, Edward L. 1958 physiology/medicine U.S. genetic regulation of chemical processesTaube, Henry 1983 chemistry U.S. study of electron transfer reactionsTaylor, Joseph H., Jr. 1993 physics U.S. identifying binary pulsarsTaylor, Richard E. 1990 physics Canada discovery of atomic quarksTemin, Howard Martin 1975 physiology/medicine U.S. interaction between tumour viruses and the genetic material of the cellTeresa, Mother (Teresa, Blessed Mother) 1979 peace IndiaTheiler, Max 1951 physiology/medicine South Africa yellow fever discoveriesTheorell, Axel Hugo Teodor 1955 physiology/medicine Sweden nature and mode of action of oxidation enzymesThomas, E. Donnall 1990 physiology/medicine U.S. development of kidney and bone-marrow transplantsThomson, Sir George Paget 1937 physics U.K. experimental demonstration of the interference phenomenon in crystals irradiated by electronsThomson, Sir J.J. 1906 physics U.K. researches into electrical conductivity of gasesTinbergen, Jan 1969 economics The Netherlands work in econometricsTinbergen, Nikolaas 1973 physiology/medicine U.K. discoveries in animal behaviour patternsTing, Samuel C.C. 1976 physics U.S. discovery of new class of elementary particles (psi, or J)Tiselius, Arne 1948 chemistry Sweden researches in electrophoresis and adsorption analysis; serum proteinsTobin, James 1981 economics U.S. portfolio selection theory of investmentTodd (of Trumpington), Alexander Robertus Todd, Baron (Todd, Alexander Robertus Todd, Baron) 1957 chemistry U.K. work on nucleotides and nucleotide coenzymesTomonaga Shin'ichiro (Tomonaga Shin'ichirō) 1965 physics Japan basic principles of quantum electrodynamicsTonegawa Susumu 1987 physiology/medicine Japan study of genetic aspects of antibodiesTownes, Charles Hard 1964 physics U.S. work in quantum electronics leading to construction of instruments based on maser-laser principlesTrimble, David 1998 peace Northern IrelandTsien, Roger Y. 2008 physics U.S. discovery and development of the green fluorescent protein, GFPTsui, Daniel C. 1998 physics U.S. discovery of fractional quantum Hall effectTutu, Desmond 1984 peace South AfricaUndset, Sigrid 1928 literature Norway novelistUnited Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) 1965 peace (founded 1946)United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, Office of the 1954 peace (founded 1951)United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, Office of the 1981 peace (founded 1951)United Nations Peacekeeping Forces 1988 peaceUrey, Harold C. 1934 chemistry U.S. discovery of heavy hydrogen*Nationality given is the citizenship of recipient at the time award was made. Prizes may be withheld or not awarded in years when no worthy recipient can be found or when the world situation (e.g., World Wars I and II) prevents the gathering of information needed to reach a decision.TopBack to Nobel Prize winners directorySee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
