- Properties of the halogen elements
-
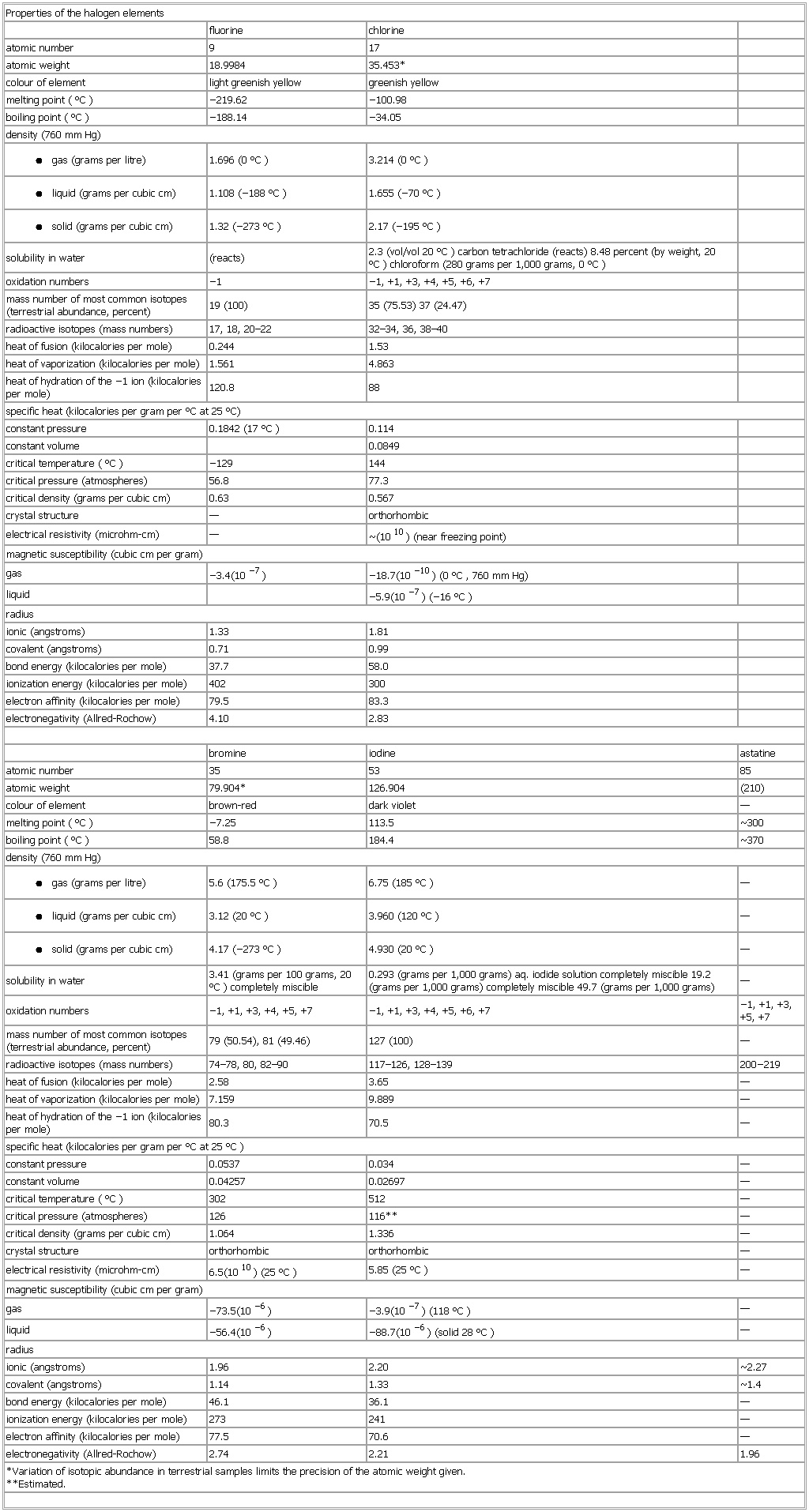
▪ TableProperties of the halogen elementsfluorine chlorineatomic number 9 17atomic weight 18.9984 35.453*colour of element light greenish yellow greenish yellowmelting point (°C) −219.62 −100.98boiling point (°C) −188.14 −34.05density (760 mm Hg)● gas (grams per litre)1.696 (0 °C) 3.214 (0 °C)● liquid (grams per cubic cm)1.108 (−188 °C) 1.655 (−70 °C)● solid (grams per cubic cm)1.32 (−273 °C) 2.17 (−195 °C)solubility in water (reacts) 2.3 (vol/vol 20 °C) carbon tetrachloride (reacts) 8.48 percent (by weight, 20 °C) chloroform (280 grams per 1,000 grams, 0 °C)oxidation numbers −1 −1, +1, +3, +4, +5, +6, +7mass number of most common isotopes (terrestrial abundance, percent) 19 (100) 35 (75.53) 37 (24.47)radioactive isotopes (mass numbers) 17, 18, 20–22 32–34, 36, 38–40heat of fusion (kilocalories per mole) 0.244 1.53heat of vaporization (kilocalories per mole) 1.561 4.863heat of hydration of the −1 ion (kilocalories per mole) 120.8 88specific heat (kilocalories per gram per °C at 25 °C)constant pressure 0.1842 (17 °C) 0.114constant volume 0.0849critical temperature (°C) −129 144critical pressure (atmospheres) 56.8 77.3critical density (grams per cubic cm) 0.63 0.567crystal structure — orthorhombicelectrical resistivity (microhm-cm) — Properties of the halogen elements(1010) (near freezing point)magnetic susceptibility (cubic cm per gram)gas −3.4(10−7) −18.7(10−10) (0 °C, 760 mm Hg)liquid −5.9(10−7) (−16 °C)radiusionic (angstroms) 1.33 1.81covalent (angstroms) 0.71 0.99bond energy (kilocalories per mole) 37.7 58.0ionization energy (kilocalories per mole) 402 300electron affinity (kilocalories per mole) 79.5 83.3electronegativity (Allred-Rochow) 4.10 2.83bromine iodine astatineatomic number 35 53 85atomic weight 79.904* 126.904 (210)colour of element brown-red dark violet —melting point (°C) −7.25 113.5 Properties of the halogen elements300boiling point (°C) 58.8 184.4 Properties of the halogen elements370density (760 mm Hg)● gas (grams per litre)5.6 (175.5 °C) 6.75 (185 °C) —● liquid (grams per cubic cm)3.12 (20 °C) 3.960 (120 °C) —● solid (grams per cubic cm)4.17 (−273 °C) 4.930 (20 °C) —solubility in water 3.41 (grams per 100 grams, 20 °C) completely miscible 0.293 (grams per 1,000 grams) aq. iodide solution completely miscible 19.2 (grams per 1,000 grams) completely miscible 49.7 (grams per 1,000 grams) —oxidation numbers −1, +1, +3, +4, +5, +7 −1, +1, +3, +4, +5, +6, +7 −1, +1, +3, +5, +7mass number of most common isotopes (terrestrial abundance, percent) 79 (50.54), 81 (49.46) 127 (100) —radioactive isotopes (mass numbers) 74–78, 80, 82–90 117–126, 128–139 200−219heat of fusion (kilocalories per mole) 2.58 3.65 —heat of vaporization (kilocalories per mole) 7.159 9.889 —heat of hydration of the −1 ion (kilocalories per mole) 80.3 70.5 —specific heat (kilocalories per gram per °C at 25 °C)constant pressure 0.0537 0.034 —constant volume 0.04257 0.02697 —critical temperature (°C) 302 512 —critical pressure (atmospheres) 126 116** —critical density (grams per cubic cm) 1.064 1.336 —crystal structure orthorhombic orthorhombic —electrical resistivity (microhm-cm) 6.5(1010) (25 °C) 5.85 (25 °C) —magnetic susceptibility (cubic cm per gram)gas −73.5(10−6) −3.9(10−7) (118 °C) —liquid −56.4(10−6) −88.7(10−6) (solid 28 °C) —radiusionic (angstroms) 1.96 2.20 Properties of the halogen elements2.27covalent (angstroms) 1.14 1.33 Properties of the halogen elements1.4bond energy (kilocalories per mole) 46.1 36.1 —ionization energy (kilocalories per mole) 273 241 —electron affinity (kilocalories per mole) 77.5 70.6 —electronegativity (Allred-Rochow) 2.74 2.21 1.96*Variation of isotopic abundance in terrestrial samples limits the precision of the atomic weight given.**Estimated.See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
