Some typical occurrences of the rock-forming feldspars
- Some typical occurrences of the rock-forming feldspars
-
Some typical occurrences
of the rock-forming feldspars
Potassium feldspars*
sanidine potassium-rich volcanic rocks and near-surface minor intrusions—e.g., rhyolites, trachytes, and high-temperature contact metamorphic rocks
orthoclase potassium-rich dike rocks—e.g., rhyolite and trachyte porphyries; granites, granodiorites, and syenites**; moderate- to high-grade metamorphic gneisses and schists; and sandstones
microcline granitic pegmatites, hydrothermal veins; granites, granodiorites, and syenites**; low- to moderate-grade metamorphic rocks; sandstones and conglomerates
Plagioclase feldspars
albite granites; granitic pegmatites; low-grade metamorphic gneisses and schists; sandstones
oligoclase granodiorites and monzonites; sandstones; moderate-grade metamorphic rocks
andesine diorites; andesites; moderate-grade meta-morphic rocks, especially amphibolites
labradorite gabbros and anorthosites***; diabases and basalts
bytownite gabbros and anorthosites***; diabases and basalts
anorthite gabbros; contact-metamorphosed impure limestones; and high-grade metamorphic rocks
*
Including perthites.
In addition,
anorthoclase occurs only in a few rather abnormal syenites (
e.
g.,
larvikite),
and adularia—
transparent,
colourless to white,
commonly opalescent potassium feldspar with a pseudo rhombohedral habit—
occurs in some low-
temperature hydrothermal veins. **
Typical syenites consist of nearly 90 percent alkali feldspar. ***
Typical anorthosites consist of about 90 percent plagioclase feldspar.
See as table: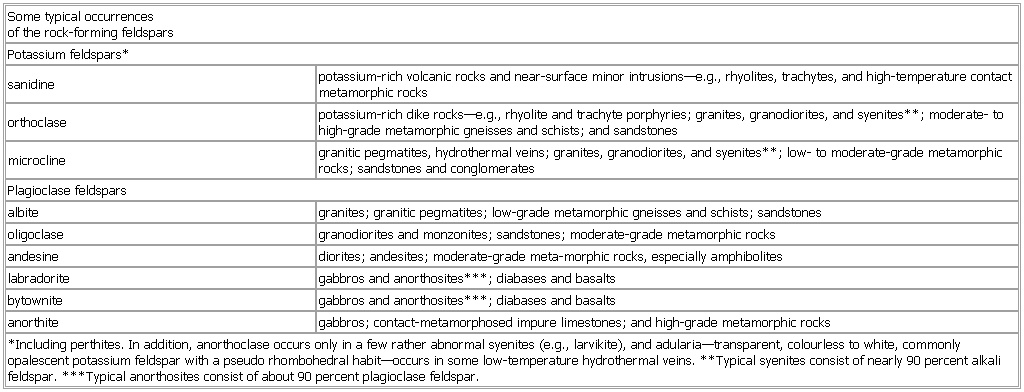
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
feldspar — /feld spahr , fel /, n. any of a group of minerals, principally aluminosilicates of potassium, sodium, and calcium, characterized by two cleavages at nearly right angles: one of the most important constituents of igneous rocks. Also, felspar.… … Universalium
igneous rock — Any of various crystalline or glassy, noncrystalline rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten earth material (magma). Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary … Universalium
metamorphic rock — Any of a class of rocks that result from the alteration of preexisting rocks in response to changing geological conditions, including variations in temperature, pressure, and mechanical stress. The preexisting rocks may be igneous, sedimentary,… … Universalium
chemical element — Introduction also called element, any substance that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by ordinary chemical processes. Elements are the fundamental materials of which all matter is composed. This article considers the… … Universalium
dolomite — dolomitic /dol euh mit ik/, adj. /doh leuh muyt , dol euh /, n. 1. a very common mineral, calcium magnesium carbonate, CaMg(CO3)2, occurring in crystals and in masses. 2. a rock consisting essentially or largely of this mineral. [1785 95; < F,… … Universalium
Earth Sciences — ▪ 2009 Introduction Geology and Geochemistry The theme of the 33rd International Geological Congress, which was held in Norway in August 2008, was “Earth System Science: Foundation for Sustainable Development.” It was attended by nearly… … Universalium

