- Phosphate minerals
-
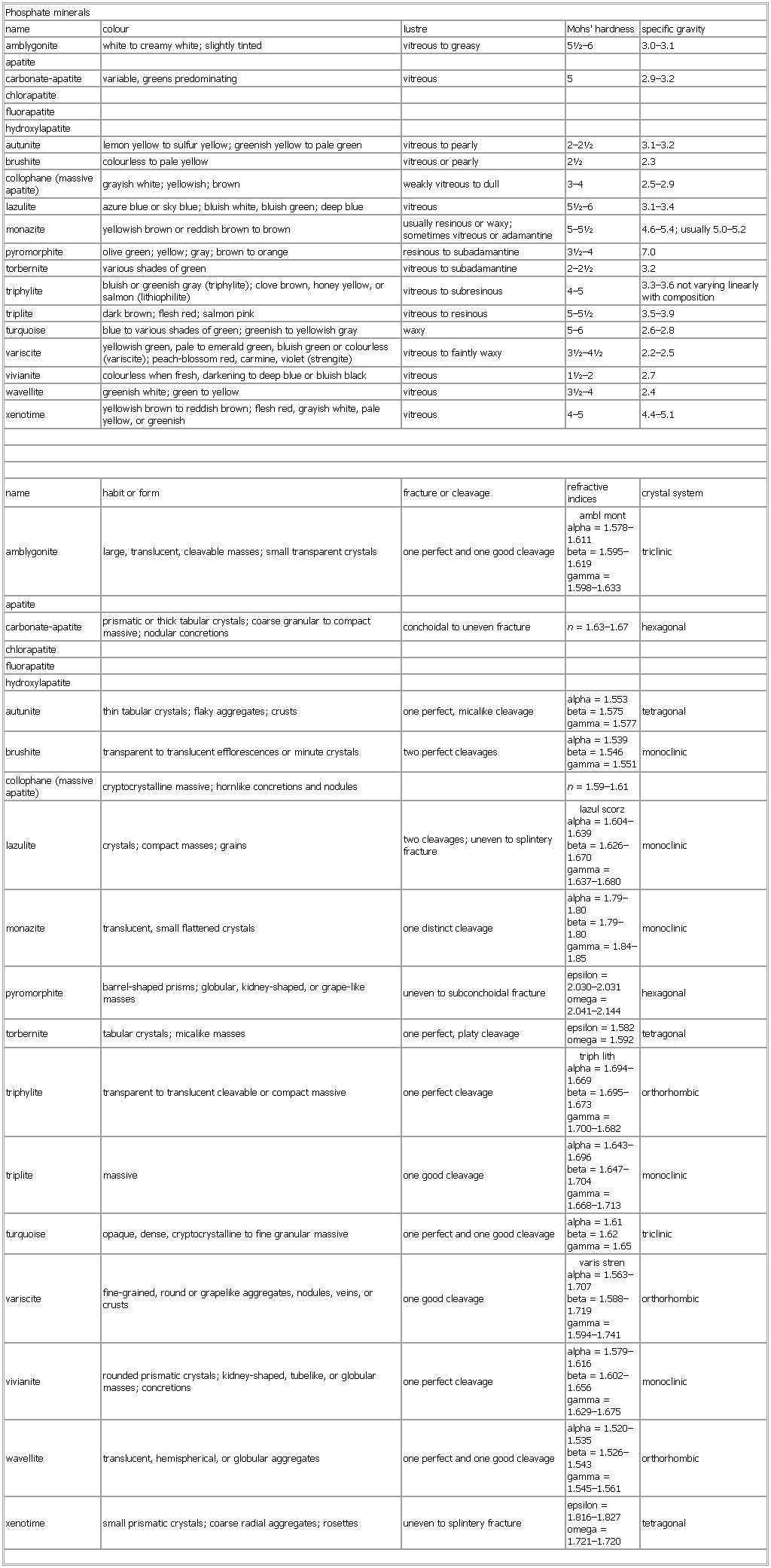
▪ TablePhosphate mineralsname colour lustre Mohs' hardness specific gravityamblygonite white to creamy white; slightly tinted vitreous to greasy 5½–6 3.0–3.1apatitecarbonate-apatite variable, greens predominating vitreous 5 2.9–3.2chlorapatitefluorapatitehydroxylapatiteautunite lemon yellow to sulfur yellow; greenish yellow to pale green vitreous to pearly 2–2½ 3.1–3.2brushite colourless to pale yellow vitreous or pearly 2½ 2.3collophane (massive apatite) grayish white; yellowish; brown weakly vitreous to dull 3–4 2.5–2.9lazulite azure blue or sky blue; bluish white, bluish green; deep blue vitreous 5½–6 3.1–3.4monazite yellowish brown or reddish brown to brown usually resinous or waxy; sometimes vitreous or adamantine 5–5½ 4.6–5.4; usually 5.0–5.2pyromorphite olive green; yellow; gray; brown to orange resinous to subadamantine 3½–4 7.0torbernite various shades of green vitreous to subadamantine 2–2½ 3.2triphylite bluish or greenish gray (triphylite); clove brown, honey yellow, or salmon (lithiophilite) vitreous to subresinous 4–5 3.3–3.6 not varying linearly with compositiontriplite dark brown; flesh red; salmon pink vitreous to resinous 5–5½ 3.5–3.9turquoise blue to various shades of green; greenish to yellowish gray waxy 5–6 2.6–2.8variscite yellowish green, pale to emerald green, bluish green or colourless (variscite); peach-blossom red, carmine, violet (strengite) vitreous to faintly waxy 3½–4½ 2.2–2.5vivianite colourless when fresh, darkening to deep blue or bluish black vitreous 1½–2 2.7wavellite greenish white; green to yellow vitreous 3½–4 2.4xenotime yellowish brown to reddish brown; flesh red, grayish white, pale yellow, or greenish vitreous 4–5 4.4–5.1name habit or form fracture or cleavage refractive indices crystal systemamblygonite large, translucent, cleavable masses; small transparent crystals one perfect and one good cleavage ambl montalpha = 1.578–1.611beta = 1.595–1.619gamma = 1.598–1.633 triclinicapatitecarbonate-apatite prismatic or thick tabular crystals; coarse granular to compact massive; nodular concretions conchoidal to uneven fracture n = 1.63–1.67 hexagonalchlorapatitefluorapatitehydroxylapatiteautunite thin tabular crystals; flaky aggregates; crusts one perfect, micalike cleavage alpha = 1.553beta = 1.575gamma = 1.577 tetragonalbrushite transparent to translucent efflorescences or minute crystals two perfect cleavages alpha = 1.539beta = 1.546gamma = 1.551 monocliniccollophane (massive apatite) cryptocrystalline massive; hornlike concretions and nodules n = 1.59–1.61lazulite crystals; compact masses; grains two cleavages; uneven to splintery fracture lazul scorzalpha = 1.604–1.639beta = 1.626–1.670gamma = 1.637–1.680 monoclinicmonazite translucent, small flattened crystals one distinct cleavage alpha = 1.79–1.80beta = 1.79–1.80gamma = 1.84–1.85 monoclinicpyromorphite barrel-shaped prisms; globular, kidney-shaped, or grape-like masses uneven to subconchoidal fracture epsilon = 2.030–2.031omega = 2.041–2.144 hexagonaltorbernite tabular crystals; micalike masses one perfect, platy cleavage epsilon = 1.582omega = 1.592 tetragonaltriphylite transparent to translucent cleavable or compact massive one perfect cleavage triph lithalpha = 1.694–1.669beta = 1.695–1.673gamma = 1.700–1.682 orthorhombictriplite massive one good cleavage alpha = 1.643–1.696beta = 1.647–1.704gamma = 1.668–1.713 monoclinicturquoise opaque, dense, cryptocrystalline to fine granular massive one perfect and one good cleavage alpha = 1.61beta = 1.62gamma = 1.65 triclinicvariscite fine-grained, round or grapelike aggregates, nodules, veins, or crusts one good cleavage varis strenalpha = 1.563–1.707beta = 1.588–1.719gamma = 1.594–1.741 orthorhombicvivianite rounded prismatic crystals; kidney-shaped, tubelike, or globular masses; concretions one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.579–1.616beta = 1.602–1.656gamma = 1.629–1.675 monoclinicwavellite translucent, hemispherical, or globular aggregates one perfect and one good cleavage alpha = 1.520–1.535beta = 1.526–1.543gamma = 1.545–1.561 orthorhombicxenotime small prismatic crystals; coarse radial aggregates; rosettes uneven to splintery fracture epsilon = 1.816–1.827omega = 1.721–1.720 tetragonalSee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
