- Animal diseases usually confined to certain regions of the world
-
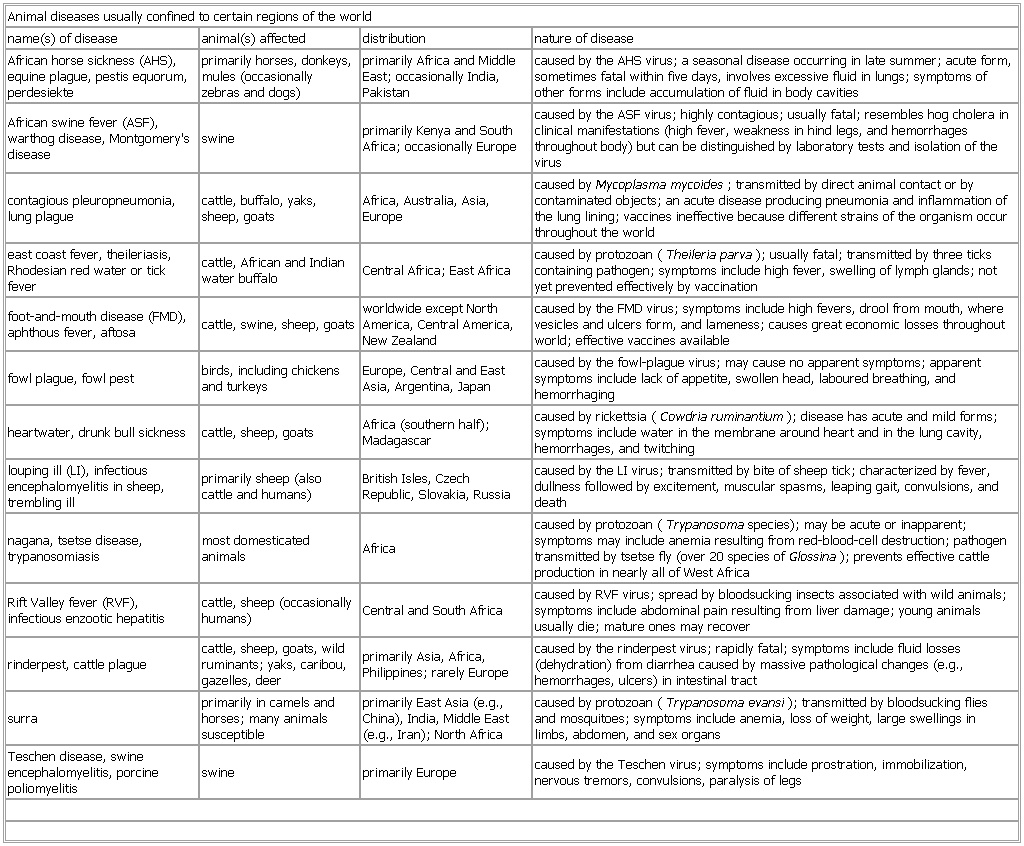
▪ TableAnimal diseases usually confined to certain regions of the worldname(s) of disease animal(s) affected distribution nature of diseaseAfrican horse sickness (AHS), equine plague, pestis equorum, perdesiekte primarily horses, donkeys, mules (occasionally zebras and dogs) primarily Africa and Middle East; occasionally India, Pakistan caused by the AHS virus; a seasonal disease occurring in late summer; acute form, sometimes fatal within five days, involves excessive fluid in lungs; symptoms of other forms include accumulation of fluid in body cavitiesAfrican swine fever (ASF), warthog disease, Montgomery's disease swine primarily Kenya and South Africa; occasionally Europe caused by the ASF virus; highly contagious; usually fatal; resembles hog cholera in clinical manifestations (high fever, weakness in hind legs, and hemorrhages throughout body) but can be distinguished by laboratory tests and isolation of the viruscontagious pleuropneumonia, lung plague cattle, buffalo, yaks, sheep, goats Africa, Australia, Asia, Europe caused by Mycoplasma mycoides; transmitted by direct animal contact or by contaminated objects; an acute disease producing pneumonia and inflammation of the lung lining; vaccines ineffective because different strains of the organism occur throughout the worldeast coast fever, theileriasis, Rhodesian red water or tick fever cattle, African and Indian water buffalo Central Africa; East Africa caused by protozoan (Theileria parva); usually fatal; transmitted by three ticks containing pathogen; symptoms include high fever, swelling of lymph glands; not yet prevented effectively by vaccinationfoot-and-mouth disease (FMD), aphthous fever, aftosa cattle, swine, sheep, goats worldwide except North America, Central America, New Zealand caused by the FMD virus; symptoms include high fevers, drool from mouth, where vesicles and ulcers form, and lameness; causes great economic losses throughout world; effective vaccines availablefowl plague, fowl pest birds, including chickens and turkeys Europe, Central and East Asia, Argentina, Japan caused by the fowl-plague virus; may cause no apparent symptoms; apparent symptoms include lack of appetite, swollen head, laboured breathing, and hemorrhagingheartwater, drunk bull sickness cattle, sheep, goats Africa (southern half); Madagascar caused by rickettsia (Cowdria ruminantium); disease has acute and mild forms; symptoms include water in the membrane around heart and in the lung cavity, hemorrhages, and twitchinglouping ill (LI), infectious encephalomyelitis in sheep, trembling ill primarily sheep (also cattle and humans) British Isles, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Russia caused by the LI virus; transmitted by bite of sheep tick; characterized by fever, dullness followed by excitement, muscular spasms, leaping gait, convulsions, and deathnagana, tsetse disease, trypanosomiasis most domesticated animals Africa caused by protozoan (Trypanosoma species); may be acute or inapparent; symptoms may include anemia resulting from red-blood-cell destruction; pathogen transmitted by tsetse fly (over 20 species of Glossina); prevents effective cattle production in nearly all of West AfricaRift Valley fever (RVF), infectious enzootic hepatitis cattle, sheep (occasionally humans) Central and South Africa caused by RVF virus; spread by bloodsucking insects associated with wild animals; symptoms include abdominal pain resulting from liver damage; young animals usually die; mature ones may recoverrinderpest, cattle plague cattle, sheep, goats, wild ruminants; yaks, caribou, gazelles, deer primarily Asia, Africa, Philippines; rarely Europe caused by the rinderpest virus; rapidly fatal; symptoms include fluid losses (dehydration) from diarrhea caused by massive pathological changes (e.g., hemorrhages, ulcers) in intestinal tractsurra primarily in camels and horses; many animals susceptible primarily East Asia (e.g., China), India, Middle East (e.g., Iran); North Africa caused by protozoan (Trypanosoma evansi); transmitted by bloodsucking flies and mosquitoes; symptoms include anemia, loss of weight, large swellings in limbs, abdomen, and sex organsTeschen disease, swine encephalomyelitis, porcine poliomyelitis swine primarily Europe caused by the Teschen virus; symptoms include prostration, immobilization, nervous tremors, convulsions, paralysis of legsSee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
