Properties of some amines
- Properties of some amines
-
Properties of some amines
RNH2 R2NH R3N
substituent group, R boiling point (°C) pKb boiling point (°C) pKb boiling point (°C) pKb
CH3 −6 3.38 7 3.36 3.5 4.24
C2H5 16.5 3.37 55.5 3.02 89.4 3.35
n-C4H9 77.8 3.41 161 2.75 214 3.11
sec-
C4H9 66 3.
44 132 2.
99
tert-C4H9 45 3.55 95
C6H5 184.4* 4.59 302** 0.85 365*** <0
*Melting point −6.24 °C. **Melting point 52.8 °C. ***Melting point 127 °C.
See as table: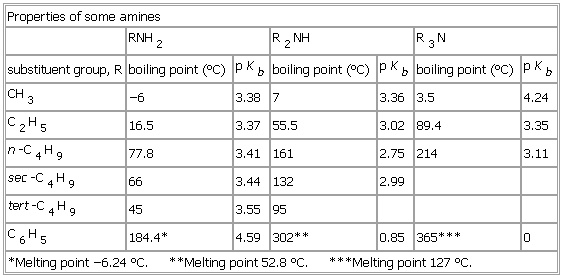
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
amine — aminic /euh mee nik, euh min ik/, adj. aminity /euh min i tee/, n. /euh meen , am in/, n. Chem. any of a class of compounds derived from ammonia by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. [1860 65; AM(MONIUM) + INE2] * * *… … Universalium
Ligand — This article is about ligands in inorganic chemistry. For ligands in biochemistry, see Ligand (biochemistry). For other uses, see Ligand (disambiguation). Cobalt complex [HCo(CO)4] with five ligands In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion… … Wikipedia
Heterocyclic compound — Heterocyclic compounds are organic compounds containing at least one atom of carbon, and at least one element other than carbon, such as sulfur, oxygen or nitrogen within a ring structure .cite book author = Eicher, T.; Hauptmann, S. title = The… … Wikipedia
Mathematics and Physical Sciences — ▪ 2003 Introduction Mathematics Mathematics in 2002 was marked by two discoveries in number theory. The first may have practical implications; the second satisfied a 150 year old curiosity. Computer scientist Manindra Agrawal of the… … Universalium
Accelerant — Accelerants play a major role in chemistry. Most chemical reactions can be hastened with an accelerant. Accelerants are catalysts which alter a chemical bond, speed up a chemical process, or bring organisms back to homeostasis. An accelerant can… … Wikipedia
Dimethocaine — Systematic (IUPAC) name (3 diethylamino 2,2 dimethylpropyl) 4 aminobenzoate Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? … Wikipedia
chemical compound — Introduction any substance composed of identical molecules consisting of atoms (atom) of two or more chemical elements (chemical element). All the matter in the universe is composed of the atoms of more than 100 different chemical elements … Universalium
Amine — For other uses, see Amine (disambiguation). Primary amine Secondary amine Tertiary amine … Wikipedia
acid–base reaction — ▪ chemistry Introduction a type of chemical process typified by the exchange of one or more hydrogen ions, H+, between species that may be neutral (molecules, such as water, H2O; or acetic acid, CH3CO2H) or electrically charged (ions, such… … Universalium
Ethylene oxide — Oxirane redirects here. For oxiranes as a class of molecules, see epoxide. Ethylene oxide … Wikipedia

