Typical capacities of urban mass transportation modes
- Typical capacities of urban mass transportation modes
-
Typical capacities of urban mass transportation modes
persons per vehicle "trains" per hour passengers per hour
vehicle type guideway type seated crowded "train" length low high average speed low high
auto streets 1.2 3 1 450 900 20 540 2,700
auto freeways 1.2 3 1 900 1,800 30 1,080 5,400
bus streets 50 80 1 1 60 8 50 4,800
bus separate 50 80 1 1 30 20 50 2,400
light rail streets 80 100 3 6 30 10 1,440 9,000
light rail separate 90 120 4 4 30 25 1,440 14,400
heavy rail separate 100 120 8 4 40 30 3,200 38,400
commuter rail separate 100 150 10 1 12 35 1,000 18,000
See as table: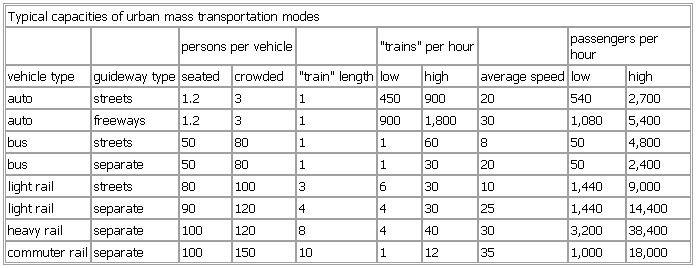
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
mass transit — a system of large scale public transportation in a given metropolitan area, typically comprising buses, subways, and elevated trains. Cf. rapid transit. * * * Transportation systems, usually publicly but sometimes privately owned and operated,… … Universalium
Personal rapid transit — ation concept that offers on demand, non stop transportation, using small, independent vehicles on a network of specially built guideways. Several different designs have been proposed, and as of 2008, at least one is under… … Wikipedia
Business and Industry Review — ▪ 1999 Introduction Overview Annual Average Rates of Growth of Manufacturing Output, 1980 97, Table Pattern of Output, 1994 97, Table Index Numbers of Production, Employment, and Productivity in Manufacturing Industries, Table (For Annual… … Universalium
Montreal Metro — Not to be confused with Greater Montreal. Montreal Metro Info … Wikipedia
locomotive — locomotively, adv. locomotiveness, locomotivity, n. /loh keuh moh tiv/, n. 1. a self propelled, vehicular engine, powered by steam, a diesel, or electricity, for pulling or, sometimes, pushing a train or individual railroad cars. 2. an organized… … Universalium
Europe, history of — Introduction history of European peoples and cultures from prehistoric times to the present. Europe is a more ambiguous term than most geographic expressions. Its etymology is doubtful, as is the physical extent of the area it designates.… … Universalium
Italy — /it l ee/, n. a republic in S Europe, comprising a peninsula S of the Alps, and Sicily, Sardinia, Elba, and other smaller islands: a kingdom 1870 1946. 57,534,088; 116,294 sq. mi. (301,200 sq. km). Cap.: Rome. Italian, Italia. * * * Italy… … Universalium
France — /frans, frahns/; Fr. /frddahonns/, n. 1. Anatole /ann nann tawl /, (Jacques Anatole Thibault), 1844 1924, French novelist and essayist: Nobel prize 1921. 2. a republic in W Europe. 58,470,421; 212,736 sq. mi. (550,985 sq. km). Cap.: Paris. 3.… … Universalium
education — /ej oo kay sheuhn/, n. 1. the act or process of imparting or acquiring general knowledge, developing the powers of reasoning and judgment, and generally of preparing oneself or others intellectually for mature life. 2. the act or process of… … Universalium
Elevator — For other uses, see Elevator (disambiguation). A set of lifts in the lower level of a London Underground station. The arrows indicate each elevator s position and direction of travel … Wikipedia

