- Pyroxenes
-
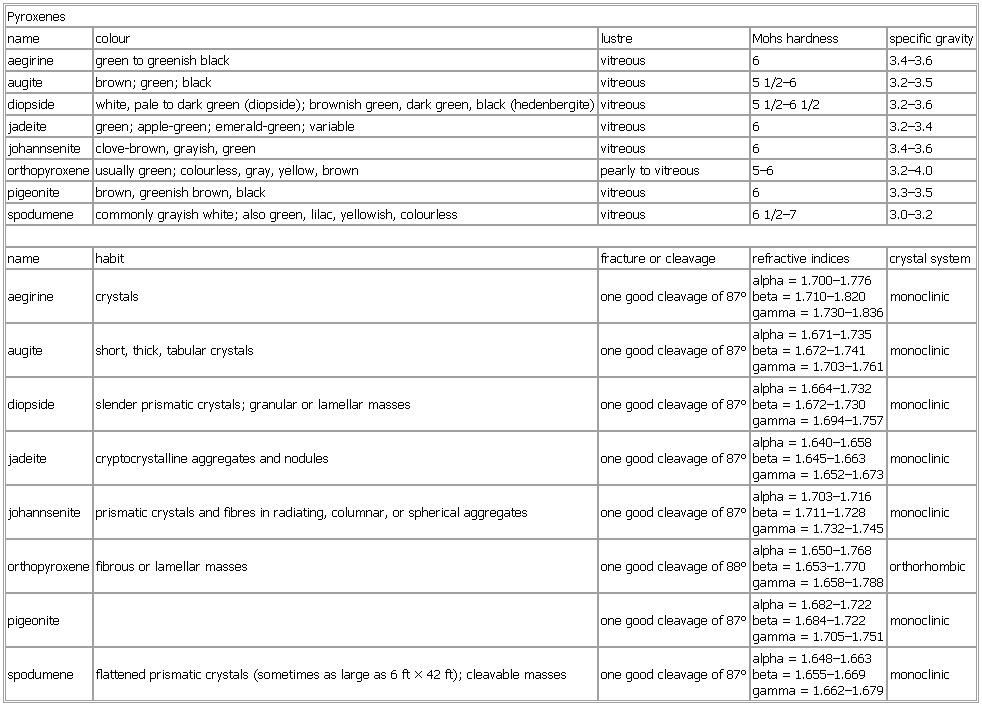
▪ TablePyroxenesname colour lustre Mohs hardness specific gravityaegirine green to greenish black vitreous 6 3.4–3.6augite brown; green; black vitreous 5 1/2–6 3.2–3.5diopside white, pale to dark green (diopside); brownish green, dark green, black (hedenbergite) vitreous 5 1/2–6 1/2 3.2–3.6jadeite green; apple-green; emerald-green; variable vitreous 6 3.2–3.4johannsenite clove-brown, grayish, green vitreous 6 3.4–3.6orthopyroxene usually green; colourless, gray, yellow, brown pearly to vitreous 5–6 3.2–4.0pigeonite brown, greenish brown, black vitreous 6 3.3–3.5spodumene commonly grayish white; also green, lilac, yellowish, colourless vitreous 6 1/2–7 3.0–3.2name habit fracture or cleavage refractive indices crystal systemaegirine crystals one good cleavage of 87° alpha = 1.700–1.776beta = 1.710–1.820gamma = 1.730–1.836 monoclinicaugite short, thick, tabular crystals one good cleavage of 87° alpha = 1.671–1.735beta = 1.672–1.741gamma = 1.703–1.761 monoclinicdiopside slender prismatic crystals; granular or lamellar masses one good cleavage of 87° alpha = 1.664–1.732beta = 1.672–1.730gamma = 1.694–1.757 monoclinicjadeite cryptocrystalline aggregates and nodules one good cleavage of 87° alpha = 1.640–1.658beta = 1.645–1.663gamma = 1.652–1.673 monoclinicjohannsenite prismatic crystals and fibres in radiating, columnar, or spherical aggregates one good cleavage of 87° alpha = 1.703–1.716beta = 1.711–1.728gamma = 1.732–1.745 monoclinicorthopyroxene fibrous or lamellar masses one good cleavage of 88° alpha = 1.650–1.768beta = 1.653–1.770gamma = 1.658–1.788 orthorhombicpigeonite one good cleavage of 87° alpha = 1.682–1.722beta = 1.684–1.722gamma = 1.705–1.751 monoclinicspodumene flattened prismatic crystals (sometimes as large as 6 ft × 42 ft); cleavable masses one good cleavage of 87° alpha = 1.648–1.663beta = 1.655–1.669gamma = 1.662–1.679 monoclinicSee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
