- Major commercial lasers
-
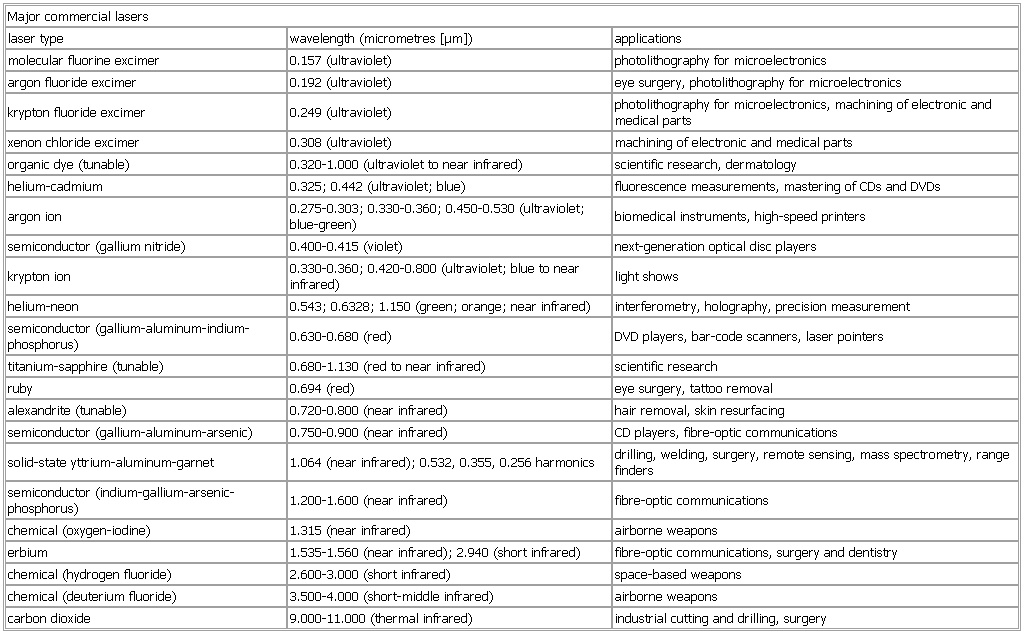
▪ TableMajor commercial laserslaser type wavelength (micrometres [μm]) applicationskrypton fluoride excimer 0.249 (ultraviolet) photolithography for microelectronics, machining of electronic and medical partshelium-cadmium 0.325; 0.442 (ultraviolet; blue) fluorescence measurements, mastering of CDs and DVDsargon ion 0.275-0.303; 0.330-0.360; 0.450-0.530 (ultraviolet; blue-green) biomedical instruments, high-speed printershelium-neon 0.543; 0.6328; 1.150 (green; orange; near infrared) interferometry, holography, precision measurementsemiconductor (gallium-aluminum-indium-phosphorus) 0.630-0.680 (red) DVD players, bar-code scanners, laser pointerssemiconductor (gallium-aluminum-arsenic) 0.750-0.900 (near infrared) CD players, fibre-optic communicationssolid-state yttrium-aluminum-garnet 1.064 (near infrared); 0.532, 0.355, 0.256 harmonics drilling, welding, surgery, remote sensing, mass spectrometry, range finderssemiconductor (indium-gallium-arsenic-phosphorus) 1.200-1.600 (near infrared) fibre-optic communicationschemical (oxygen-iodine) 1.315 (near infrared) airborne weaponserbium 1.535-1.560 (near infrared); 2.940 (short infrared) fibre-optic communications, surgery and dentistrychemical (deuterium fluoride) 3.500-4.000 (short-middle infrared) airborne weaponscarbon dioxide 9.000-11.000 (thermal infrared) industrial cutting and drilling, surgerySee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
