- Some properties of the carbon group elements
-
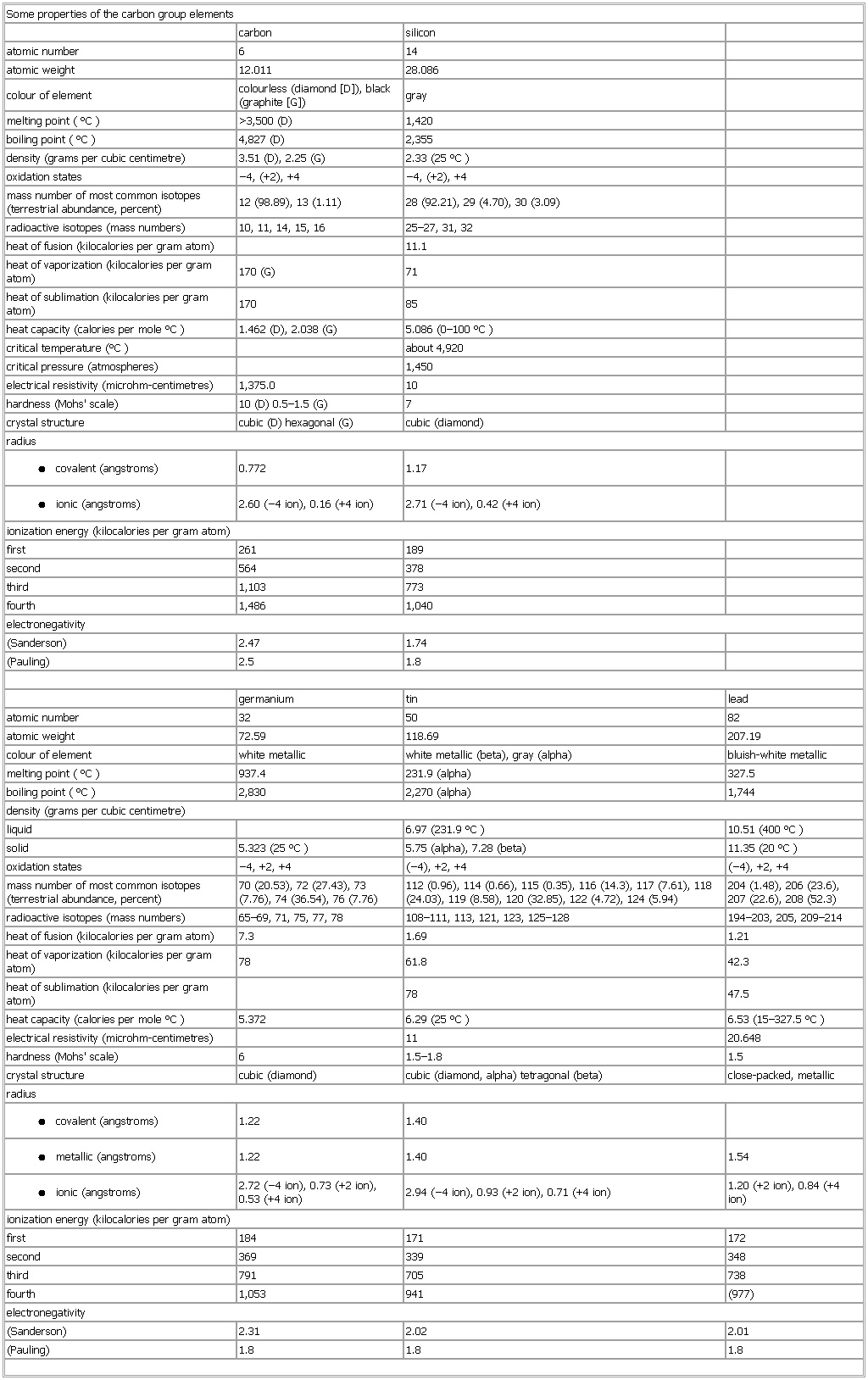
▪ TableSome properties of the carbon group elementscarbon siliconatomic number 6 14atomic weight 12.011 28.086melting point (°C) >3,500 (D) 1,420boiling point (°C) 4,827 (D) 2,355density (grams per cubic centimetre) 3.51 (D), 2.25 (G) 2.33 (25 °C)oxidation states −4, (+2), +4 −4, (+2), +4mass number of most common isotopes (terrestrial abundance, percent) 12 (98.89), 13 (1.11) 28 (92.21), 29 (4.70), 30 (3.09)radioactive isotopes (mass numbers) 10, 11, 14, 15, 16 25–27, 31, 32heat of fusion (kilocalories per gram atom) 11.1heat of vaporization (kilocalories per gram atom) 170 (G) 71heat of sublimation (kilocalories per gram atom) 170 85heat capacity (calories per mole °C) 1.462 (D), 2.038 (G) 5.086 (0–100 °C)critical temperature (°C) about 4,920critical pressure (atmospheres) 1,450electrical resistivity (microhm-centimetres) 1,375.0 10hardness (Mohs' scale) 10 (D) 0.5–1.5 (G) 7radius● covalent (angstroms)0.772 1.17● ionic (angstroms)2.60 (−4 ion), 0.16 (+4 ion) 2.71 (−4 ion), 0.42 (+4 ion)ionization energy (kilocalories per gram atom)first 261 189second 564 378third 1,103 773fourth 1,486 1,040electronegativity(Sanderson) 2.47 1.74germanium tin leadatomic number 32 50 82atomic weight 72.59 118.69 207.19density (grams per cubic centimetre)liquid 6.97 (231.9 °C) 10.51 (400 °C)oxidation states −4, +2, +4 (−4), +2, +4 (−4), +2, +4mass number of most common isotopes (terrestrial abundance, percent) 70 (20.53), 72 (27.43), 73 (7.76), 74 (36.54), 76 (7.76) 112 (0.96), 114 (0.66), 115 (0.35), 116 (14.3), 117 (7.61), 118 (24.03), 119 (8.58), 120 (32.85), 122 (4.72), 124 (5.94) 204 (1.48), 206 (23.6), 207 (22.6), 208 (52.3)radioactive isotopes (mass numbers) 65–69, 71, 75, 77, 78 108–111, 113, 121, 123, 125–128 194–203, 205, 209–214heat of fusion (kilocalories per gram atom) 7.3 1.69 1.21heat of vaporization (kilocalories per gram atom) 78 61.8 42.3heat of sublimation (kilocalories per gram atom) 78 47.5heat capacity (calories per mole °C) 5.372 6.29 (25 °C) 6.53 (15–327.5 °C)electrical resistivity (microhm-centimetres) 11 20.648hardness (Mohs' scale) 6 1.5–1.8 1.5radius● covalent (angstroms)1.22 1.40● metallic (angstroms)1.22 1.40 1.54● ionic (angstroms)2.72 (−4 ion), 0.73 (+2 ion), 0.53 (+4 ion) 2.94 (−4 ion), 0.93 (+2 ion), 0.71 (+4 ion) 1.20 (+2 ion), 0.84 (+4 ion)ionization energy (kilocalories per gram atom)first 184 171 172second 369 339 348third 791 705 738fourth 1,053 941 (977)electronegativity(Sanderson) 2.31 2.02 2.01See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
