Historical determinations of the Earth's radius and flattening
- Historical determinations of the Earth's radius and flattening
-
Historical determinations of the Earth's radius and flattening
author year method equatorial radius (in metres) l/f*
P. Bouguer and P.-L. M. de Maupertuis 1735–43 arc 6,397,300 216.80
G.B. Airy 1830 arc 6,376,542 299.30
A.R. Clarke 1866 arc 6,378,206 295.00
F.R. Helmert 1884 gravimetric 299.25
J.F. Hayford 1906 arc 6,378,283 297.80
W.A. Heiskanen 1928 gravimetric 297.00
H. Jeffreys 1948 arc 6,378,099 297.10
*Flattening denoted by f.
See as table: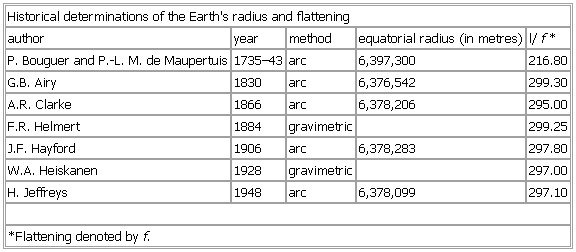
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
geoid — geoidal, adj. /jee oyd/, n. 1. an imaginary surface that coincides with mean sea level in the ocean and its extension through the continents. 2. the geometric figure formed by this surface, an ellipsoid flattened at the poles. [1880 85; < Gk… … Universalium
Moon — This article is about Earth s Moon. For moons in general, see Natural satellite. For other uses, see Moon (disambiguation) … Wikipedia
cosmos — /koz meuhs, mohs/, n., pl. cosmos, cosmoses for 2, 4. 1. the world or universe regarded as an orderly, harmonious system. 2. a complete, orderly, harmonious system. 3. order; harmony. 4. any composite plant of the genus Cosmos, of tropical… … Universalium
galaxy — /gal euhk see/, n., pl. galaxies. 1. Astron. a. a large system of stars held together by mutual gravitation and isolated from similar systems by vast regions of space. b. (usually cap.) See Milky Way. 2. any large and brilliant or impressive… … Universalium
List of Solar System objects by size — Objects in the Solar System By orbit By size By discovery date … Wikipedia

