- Dravidian cognates from representative languages
-
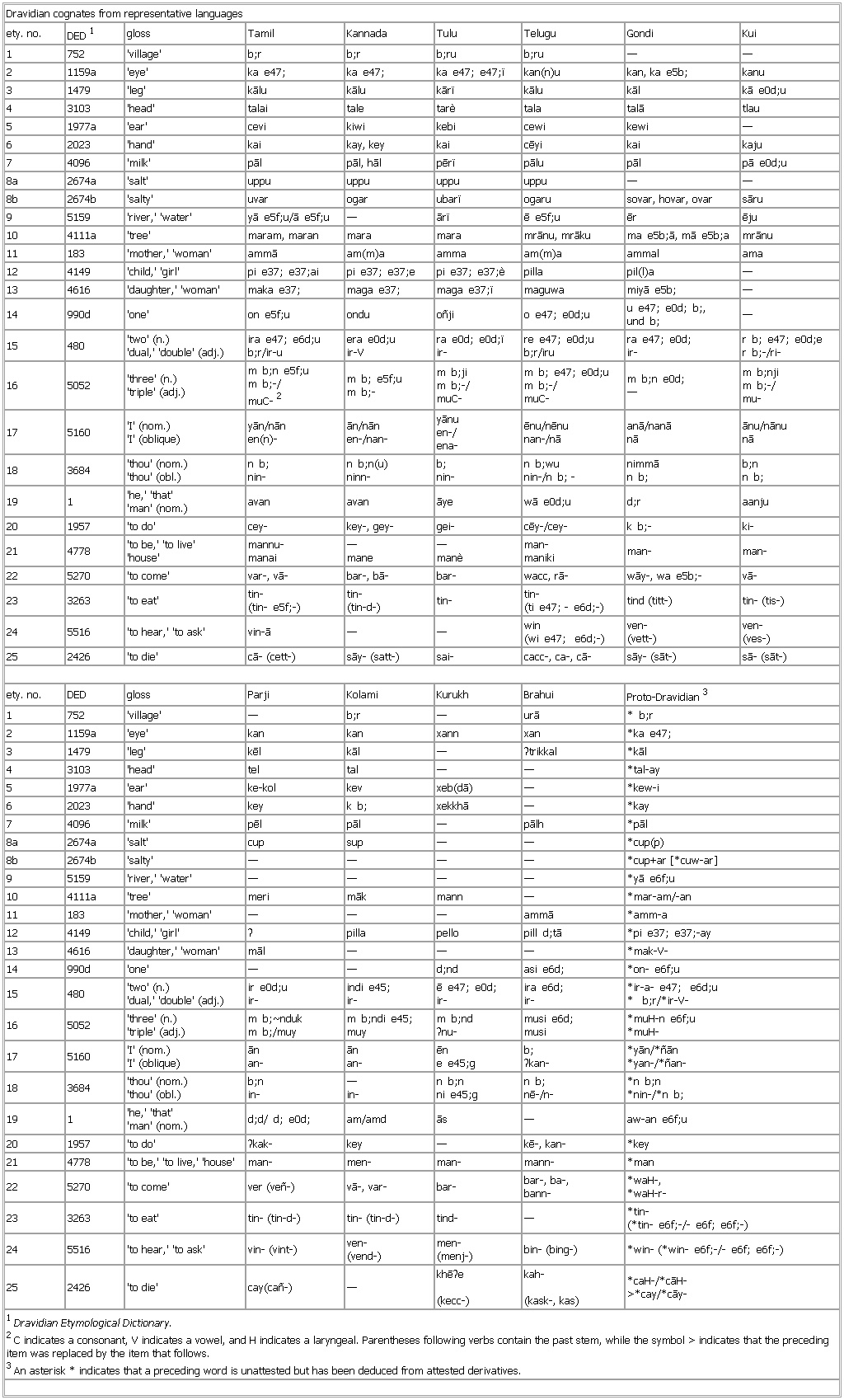
▪ TableDravidian cognates from representative languagesety. no. DED1 gloss Tamil Kannada Tulu Telugu Gondi Kui1 752 'village' b;r b;r b;ru b;ru — —2 1159a 'eye' ka e47; ka e47; ka e47; e47;ï kan(n)u kan, ka e5b; kanu3 1479 'leg' kālu kālu kārï kālu kāl kā e0d;u4 3103 'head' talai tale tarè tala talā tlau5 1977a 'ear' cevi kiwi kebi cewi kewi —6 2023 'hand' kai kay, key kai cēyi kai kaju7 4096 'milk' pāl pāl, hāl pērï pālu pāl pā e0d;u8a 2674a 'salt' uppu uppu uppu uppu — —8b 2674b 'salty' uvar ogar ubarï ogaru sovar, hovar, ovar sāru9 5159 'river,' 'water' yā e5f;u/ā e5f;u — ārï ē e5f;u ēr ēju10 4111a 'tree' maram, maran mara mara mrānu, mrāku ma e5b;ā, mā e5b;a mrānu11 183 'mother,' 'woman' ammā am(m)a amma am(m)a ammal ama12 4149 'child,' 'girl' pi e37; e37;ai pi e37; e37;e pi e37; e37;è pilla pil(l)a —13 4616 'daughter,' 'woman' maka e37; maga e37; maga e37;ï maguwa miyā e5b; —14 990d 'one' on e5f;u ondu oñji o e47; e0d;u u e47; e0d; b;,und b; —15 480 'two' (n.)b;r/ir-u era e0d;uir-V ra e0d; e0d;ïir- re e47; e0d;ub;r/iru ra e47; e0d;ir- r b; e47; e0d;er b;-/ri-16 5052 'three' (n.)m b;-/muC-2 m b; e5f;um b;- m b;jim b;-/muC- m b; e47; e0d;um b;-/muC- m b;n e0d;— m b;njim b;-/mu-en(n)- ān/nānen-/nan- yānuen-/ena- ēnu/nēnunan-/nā anā/nanānā ānu/nānunānin- n b;n(u)ninn- b;nin- n b;wunin-/n b; - nimmān b; b;nn b;19 1 'he,' 'that'20 1957 'to do' cey- key-, gey- gei- cēy-/cey- k b;- ki-21 4778 'to be,' 'to live''house' mannu-manai —mane —manè man-maniki man- man-22 5270 'to come' var-, vā- bar-, bā- bar- wacc, rā- wāy-, wa e5b;- vā-23 3263 'to eat' tin-(tin- e5f;-) tin-(tin-d-) tin- tin-(ti e47; - e6d;-) tind (titt-) tin- (tis-)24 5516 'to hear,' 'to ask' vin-ā — — win(wi e47; e6d;-) ven-(vett-) ven-(ves-)25 2426 'to die' cā- (cett-) sāy- (satt-) sai- cacc-, ca-, cā- sāy- (sāt-) sā- (sāt-)ety. no. DED gloss Parji Kolami Kurukh Brahui Proto-Dravidian31 752 'village' — b;r — urā * b;r2 1159a 'eye' kan kan xann xan *ka e47;3 1479 'leg' kēl kāl — ʔtrikkal *kāl4 3103 'head' tel tal — — *tal-ay5 1977a 'ear' ke-kol kev xeb(dā) — *kew-i6 2023 'hand' key k b; xekkhā — *kay7 4096 'milk' pēl pāl — pālh *pāl8a 2674a 'salt' cup sup — — *cup(p)8b 2674b 'salty' — — — — *cup+ar [*cuw-ar]9 5159 'river,' 'water' — — — — *yā e6f;u10 4111a 'tree' meri māk mann — *mar-am/-an11 183 'mother,' 'woman' — — — ammā *amm-a12 4149 'child,' 'girl' ʔ pilla pello pill d;tā *pi e37; e37;-ay13 4616 'daughter,' 'woman' māl — — — *mak-V-14 990d 'one' — — d;nd asi e6d; *on- e6f;u15 480 'two' (n.)ir- indi e45;ir- ē e47; e0d;ir- ira e6d;ir- *ir-a- e47; e6d;u* b;r/*ir-V-16 5052 'three' (n.)m b;/muy m b;ndi e45;muy m b;ndʔnu- musi e6d;musi *muH-n e6f;u*muH-an- ānan- ēne e45;g b;ʔkan- *yān/*ñān*yan-/*ñan-in- —in- n b;nni e45;g n b;nē-/n- *n b;n*nin-/*n b;19 1 'he,' 'that'20 1957 'to do' ʔkak- key — kē-, kan- *key21 4778 'to be,' 'to live,' 'house' man- men- man- mann- *manbann- *waH-,*waH-r-23 3263 'to eat' tin- (tin-d-) tin- (tin-d-) tind- — *tin-(*tin- e6f;-/- e6f; e6f;-)24 5516 'to hear,' 'to ask' vin- (vint-) ven-(vend-) men-(menj-) bin- (bing-) *win- (*win- e6f;-/- e6f; e6f;-)(kecc-) kah->*cay/*cāy-1Dravidian Etymological Dictionary.2C indicates a consonant, V indicates a vowel, and H indicates a laryngeal. Parentheses following verbs contain the past stem, while the symbol > indicates that the preceding item was replaced by the item that follows.3An asterisk * indicates that a preceding word is unattested but has been deduced from attested derivatives.See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
