- Amphiboles
-
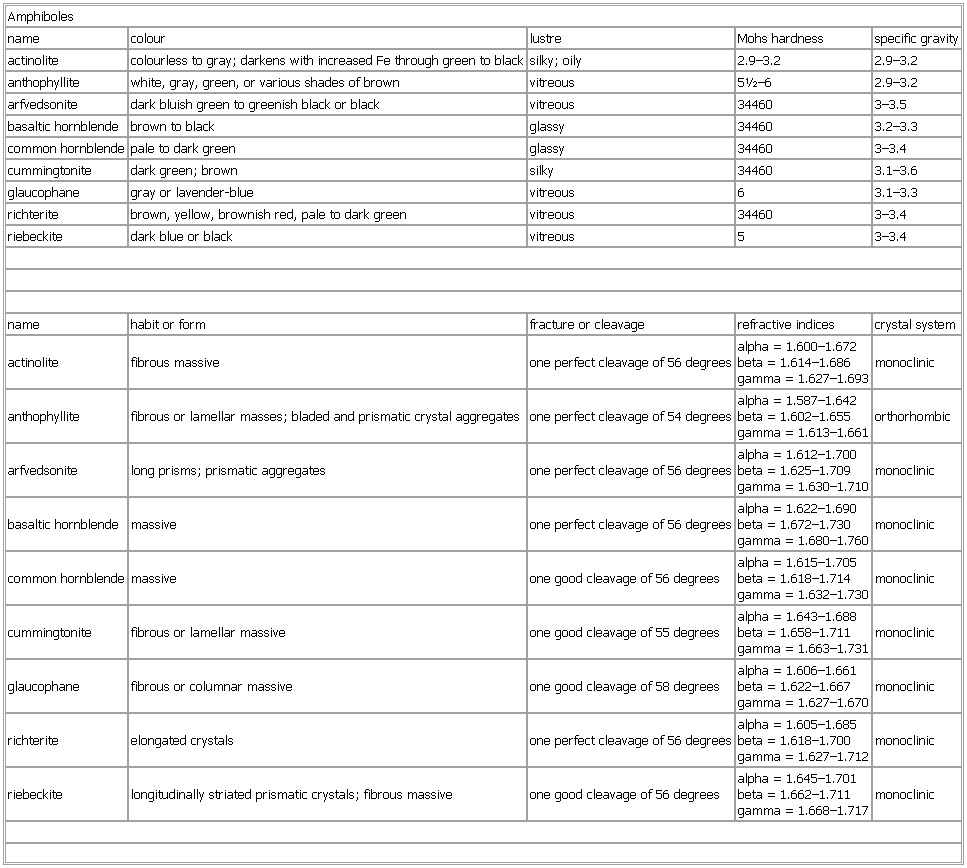
▪ TableAmphibolesname colour lustre Mohs hardness specific gravityactinolite colourless to gray; darkens with increased Fe through green to black silky; oily 2.9–3.2 2.9–3.2anthophyllite white, gray, green, or various shades of brown vitreous 5½–6 2.9–3.2arfvedsonite dark bluish green to greenish black or black vitreous 34460 3–3.5basaltic hornblende brown to black glassy 34460 3.2–3.3common hornblende pale to dark green glassy 34460 3–3.4cummingtonite dark green; brown silky 34460 3.1–3.6glaucophane gray or lavender-blue vitreous 6 3.1–3.3richterite brown, yellow, brownish red, pale to dark green vitreous 34460 3–3.4riebeckite dark blue or black vitreous 5 3–3.4name habit or form fracture or cleavage refractive indices crystal systemactinolite fibrous massive one perfect cleavage of 56 degrees alpha = 1.600–1.672beta = 1.614–1.686gamma = 1.627–1.693 monoclinicanthophyllite fibrous or lamellar masses; bladed and prismatic crystal aggregates one perfect cleavage of 54 degrees alpha = 1.587–1.642beta = 1.602–1.655gamma = 1.613–1.661 orthorhombicarfvedsonite long prisms; prismatic aggregates one perfect cleavage of 56 degrees alpha = 1.612–1.700beta = 1.625–1.709gamma = 1.630–1.710 monoclinicbasaltic hornblende massive one perfect cleavage of 56 degrees alpha = 1.622–1.690beta = 1.672–1.730gamma = 1.680–1.760 monocliniccommon hornblende massive one good cleavage of 56 degrees alpha = 1.615–1.705beta = 1.618–1.714gamma = 1.632–1.730 monocliniccummingtonite fibrous or lamellar massive one good cleavage of 55 degrees alpha = 1.643–1.688beta = 1.658–1.711gamma = 1.663–1.731 monoclinicglaucophane fibrous or columnar massive one good cleavage of 58 degrees alpha = 1.606–1.661beta = 1.622–1.667gamma = 1.627–1.670 monoclinicrichterite elongated crystals one perfect cleavage of 56 degrees alpha = 1.605–1.685beta = 1.618–1.700gamma = 1.627–1.712 monoclinicriebeckite longitudinally striated prismatic crystals; fibrous massive one good cleavage of 56 degrees alpha = 1.645–1.701beta = 1.662–1.711gamma = 1.668–1.717 monoclinicSee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
