Compositional data for selected solar system objects
- Compositional data for selected solar system objects
-
Compositional data for selected solar system objects
object distance from Sun (
AU)* mean density (g/cm
3) general composition
Sun — 1.4 hydrogen, helium
Mercury 0.4 5.4 iron, nickel, silicates
Venus 0.7 5.2 silicates, iron, nickel
Earth 1 5.5 silicates, iron, nickel
Mars 1.5 3.9 silicates, iron, sulfur
asteroids (
asteroid) 2-4.5 (main and outer belts) typically 2-4 silicates, iron, nickel
Io 5.2 3.6 silicates, sulfur
Saturn 9.5 0.7 hydrogen, helium
Titan 9.5 1.9 water ice, silicates, organics
Centaur objects (
Centaur object) 5-30 (mainly between orbits of Jupiter and Neptune) possibly less than 1 presumed similar to that of comets:
water ice, other ices, traces of silicates
Uranus 19.2 1.3 ices, silicates, hydrogen, helium
Neptune 30.1 1.6 ices, silicates, hydrogen, helium
Triton 30.1 2.0 water ice, silicates, organics
Pluto 39.5 2.0 water ice, silicates, organics
Kuiper belt objects 30-50 (main concentration) possibly less than 1 presumed similar to that of comets:
water ice, other ices, traces of silicates, organics
Oort cloud objects 20,000-100,000 possibly less than 1 presumed similar to that of comets:
water ice, other ices, traces of silicates, organics
*One astronomical unit (
AU) is the mean distance of Earth from the Sun, about 150 million km.
See as table: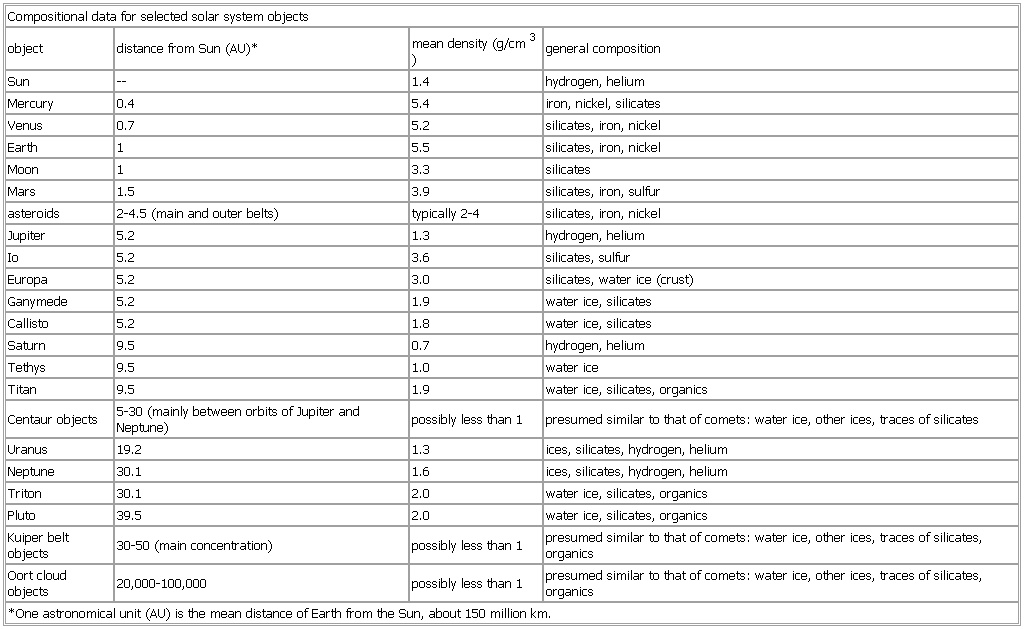
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
solar system — the sun together with all the planets and other bodies that revolve around it. [1695 1705] * * * The Sun, its planets, and the small bodies (see asteroid, Centaur object, comet, Kuiper belt, meteorite, and Oort cloud) interplanetary dust and gas… … Universalium
Solar System — This article is about the Sun and its planetary system. For other systems, see planetary system and star system. For a list of physical and orbital statistics for the Solar System s largest bodies, see List of gravitationally rounded objects of… … Wikipedia
Mars — This article is about the planet. For other uses, see Mars (disambiguation) … Wikipedia
cosmos — /koz meuhs, mohs/, n., pl. cosmos, cosmoses for 2, 4. 1. the world or universe regarded as an orderly, harmonious system. 2. a complete, orderly, harmonious system. 3. order; harmony. 4. any composite plant of the genus Cosmos, of tropical… … Universalium
asteroid — asteroidal, adj. /as teuh royd /, n. 1. Also called minor planet. Astron. any of the thousands of small bodies of from 480 miles (775 km) to less than one mile (1.6 km) in diameter that revolve about the sun in orbits lying mostly between those… … Universalium
Earth Sciences — ▪ 2009 Introduction Geology and Geochemistry The theme of the 33rd International Geological Congress, which was held in Norway in August 2008, was “Earth System Science: Foundation for Sustainable Development.” It was attended by nearly… … Universalium
Geology of Mars — Mars Mars as seen by the Hubble Space Telescope Designations … Wikipedia
Clementine (spacecraft) — This article is about the American Lunar probe. For the French satellite, see Clementine (satellite). Clementine Organization BMDO / NASA Major contractors Naval Research Laboratory Mission type … Wikipedia

