Comparison of the physical properties of molecular forms of hydrogen
- Comparison of the physical properties of molecular forms of hydrogen
-
Comparison of the physical properties of molecular forms of hydrogen
ordinary hydrogen hydrogen deuteride deuterium
gram molecular volume of the solid at the triple point (
cu cm)
23.
25 21.
84 20.
48
triple point (K) 13.96 16.60 18.73
vapour pressure at triple point (mmHg) 54.0 92.8 128.6
boiling point (K) 20.39 22.13 23.67
heat of fusion at triple point (
cal/
mole)
28.
0 38.
1 47.
0
heat of vaporization (
cal/
mole)
216*
257**
293***
*At 20.39 K.
**At 22.54 K.
***At 23.67 K.
See as table: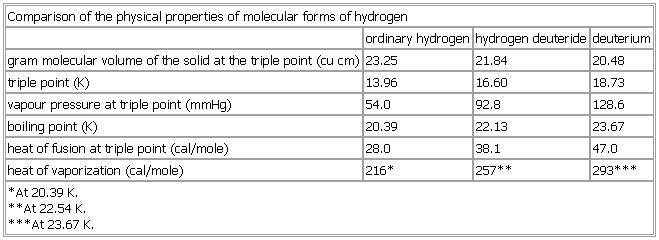
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Hydrogen peroxide — IUPAC name … Wikipedia
Molecular graphics — (MG) is the discipline and philosophy of studying molecules and their properties through graphical representation.[1] IUPAC limits the definition to representations on a graphical display device .[2] Ever since Dalton s atoms and Kekulé s benzene … Wikipedia
deuterium — /dooh tear ee euhm, dyooh /, n. Chem. an isotope of hydrogen, having twice the mass of ordinary hydrogen; heavy hydrogen. Symbol: D; at. wt.: 2.01; at. no.: 1. [1933; < Gk deúter(os) second (see DEUTERO ) + IUM] * * * or heavy hydrogen Isotope of … Universalium
physical science, principles of — Introduction the procedures and concepts employed by those who study the inorganic world. physical science, like all the natural sciences, is concerned with describing and relating to one another those experiences of the surrounding… … Universalium
Molecular nanotechnology — Part of a series of articles on Molecular Nanotechnology … Wikipedia
Molecular orbital diagram — A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram for short, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the Linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital… … Wikipedia
Hydrogen bond — A hydrogen bond results from a dipole dipole force between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom bonded to nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine (thus the name hydrogen bond , which must not be confused with a covalent bond to hydrogen). The energy… … Wikipedia
Material properties of diamond — This article addresses the material properties of diamond. For a broader discussion of diamonds, see diamond. For other uses of the word diamond, see diamond (disambiguation). Diamond An octahedral diamond crystal in matrix Gener … Wikipedia
Low molecular weight heparin — In medicine, low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is a class of medication used as an anticoagulant in diseases that feature thrombosis, as well as for prophylaxis in situations that lead to a high risk of thrombosis.[1] Thrombotic disease or… … Wikipedia
Ammonia — For other uses, see Ammonia (disambiguation). Ammonia … Wikipedia

