Physical properties of phenols
- Physical properties of phenols
-
Physical properties of phenols
common name systematic name mp (°C)
phenol benzenol 43
o-cresol 2-methylbenzenol 31
m-cresol 3-methylbenzenol 11
p-cresol 4-methylbenzenol 35
pyrocatechol benzene-1,2-diol 105
resorcinol benzene-1,3-diol 111
hydroquinone benzene-1,4-diol 171
n-hexylresorcinol 4-hexylresorcinol 69
methyl salicylate methyl 2-hydroxybenzoate −9
vanillin 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde 81
eugenol 4-allyl-2-methoxyphenol −9
thymol 5-methyl-2-isopropylphenol 51
picric acid 2,4,6-trinitrophenol 122
o-bromophenol 2-bromophenol 5
p-hydroxybenzoic acid 4-hydroxybenzoic acid 214
/TD>
common name bp (°C) solubility (
grams/100 grams water)
phenol 182 9.3
o-cresol 191 2.5
m-cresol 202 2.6
p-cresol 202 2.3
pyrocatechol 245 30
resorcinol 280 52
hydroquinone 286 6.7
n-hexylresorcinol 334 0.05
methyl salicylate 223 0.7
vanillin 285 1.0
eugenol 255
thymol 233 0.1
picric acid 1.4
o-bromophenol 194
p-hydroxybenzoic acid 8
/TD>
See as table: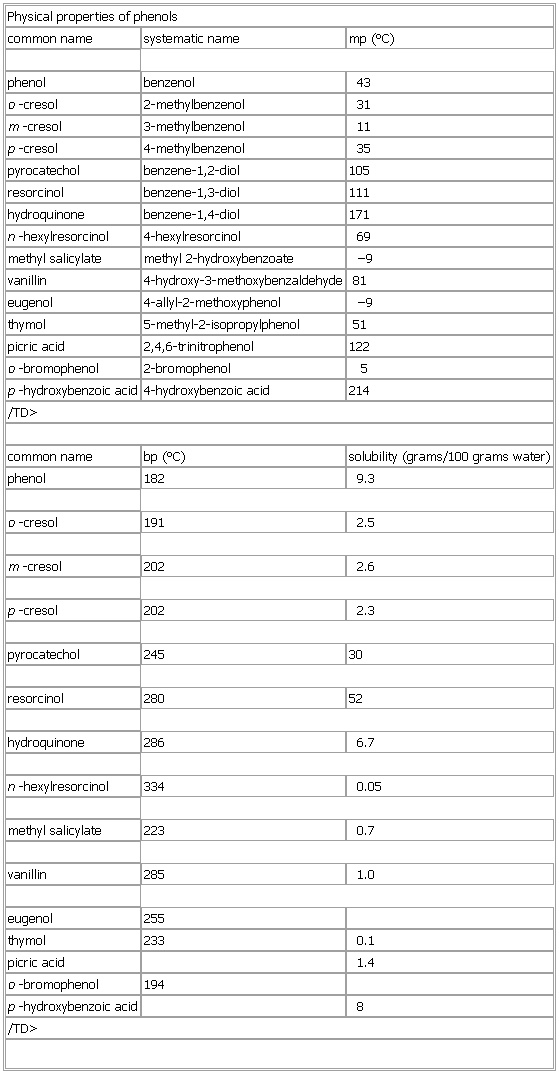
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
phenol — phenolic /fi noh lik, nol ik/, adj. /fee nawl, nol/, n. Chem. 1. Also called carbolic acid, hydroxybenzene, oxybenzene, phenylic acid. a white, crystalline, water soluble, poisonous mass, C6H5OH, obtained from coal tar, or a hydroxyl derivative… … Universalium
chemical compound — Introduction any substance composed of identical molecules consisting of atoms (atom) of two or more chemical elements (chemical element). All the matter in the universe is composed of the atoms of more than 100 different chemical elements … Universalium
Superheated water — is liquid water under pressure at temperatures between the usual boiling point (100°C) and the critical temperature (374°C). It is also known as subcritical water and pressurised hot water. Superheated water referred to in this article is stable… … Wikipedia
Cresol — Cresols are organic compounds which are methylphenols. They are a widely occurring natural and manufactured group of aromatic organic compounds which are categorized as phenols (sometimes called phenolics). Depending on the temperature, cresols… … Wikipedia
Thiol — with a blue highlighted sulfhydryl group. In organic chemistry, a thiol ( … Wikipedia
river — river1 riverless, adj. riverlike, adj. /riv euhr/, n. 1. a natural stream of water of fairly large size flowing in a definite course or channel or series of diverging and converging channels. 2. a similar stream of something other than water: a… … Universalium
Polychlorinated biphenyl — PCBs redirects here. For printed circuit boards, see printed circuit board. Labelling transformers containing PCBs … Wikipedia
Ether — This article is about a general class of organic compounds. For the specific compound, see diethyl ether. For the computer network technology, see ethernet. For the antiquated physics concept, see Luminiferous aether. For other uses, see Aether… … Wikipedia
Amino acid — This article is about the class of chemicals. For the structures and properties of the standard proteinogenic amino acids, see Proteinogenic amino acid. The generic structure of an alpha amino acid in its unionized form … Wikipedia
catalysis — catalytic /kat l it ik/, adj., n. catalytical, adj. catalytically, adv. /keuh tal euh sis/, n., pl. catalyses / seez /. 1. Chem. the causing or accelerating of a chemical change by the addition of a catalyst. 2. an action between two or more… … Universalium

