Major human blood group systems
- Major human blood group systems
-
Major human blood group systems
system date of
discovery main
antigens
ABO 1901 A1, A2, B, H
MNSs 1927 M, N, S, s
P 1927 P1, P2
Rh 1940 D, C, c, E, e
Lutheran 1945 Lua, Lub
Kell 1946 K, k
Lewis 1946 Lea, Leb
Duffy 1950 Fya, Fyb
Kidd 1951 Jka, Jkb
Diego 1955 Dia, Dib
Yt 1956 Yta, Ytb
I 1956 I, i
Xg 1962 Xga
Dombrock 1965 Doa
See as table: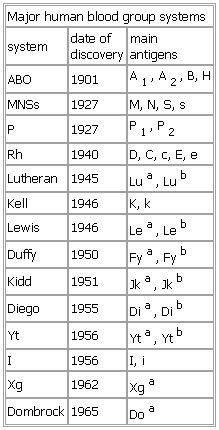
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Human blood group systems — The International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) currently recognises 30 major blood group systems (including the ABO and Rh systems). [cite web |url=http://blood.co.uk/ibgrl/ISBT%20Pages/ISBT%20Terminology%20Pages/Table%20of%20blood%20group%… … Wikipedia
blood group — Med. any of various classes into which human blood can be divided according to immunological compatibility, based on the presence or absence of specific antigens on red blood cells. Also called blood type. Cf. ABO system, Rh factor. [1915 20] * * … Universalium
Blood type — (or blood group) is determined, in part, by the ABO blood group antigens present on red blood cells. A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the… … Wikipedia
ABO blood group system — ABO redirects here. For other uses, see ABO (disambiguation). H substance redirects here. For use in inflammation, see histamine. ABO blood group antigens present on red blood cells and IgM antibodies present in the serum The ABO blood group… … Wikipedia
Blood transfusion — Intervention Plastic bag containing packed red blood cells in citrate, phosphate, dextrose, and adenine (CPDA) solution … Wikipedia
Blood substitute — A blood substitute (also called artificial blood or blood surrogates) is a substance used to mimic and fulfill some functions of biological blood, usually in the oxygen carrying sense. They aim to provide an alternative to blood transfusion,… … Wikipedia
Blood — For other uses, see Blood (disambiguation). Human blood smear: a – erythrocytes; b – neutrophil; c – eosinophil; d – lymphocyte … Wikipedia
Blood donation — Give blood redirects here. For other uses, see Give blood (disambiguation). Blood donation pictogram A blood donation occurs when a person voluntarily has blood drawn and used for transfusions or made into medications by a process called… … Wikipedia
Blood substitutes — Blood substitutes, often called artificial blood, are used to fill fluid volume and/or carry oxygen and other blood gases in the cardiovascular system. Although commonly used, the term is not accurate since human blood performs many important… … Wikipedia
International Society of Blood Transfusion — The International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT), also known as La Société Internationale de Transfusion Sanguine (SITS), is a scientific society, founded in 1935, which aims to promote the study of blood transfusion, and to spread the know… … Wikipedia

