Common Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
- Common Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
-
Common polyunsaturated fatty acids
trivial name systematic name number of carbons in chain typical sources
linoleic acid cis-
9-,
cis-
12-
octadecadienoic acid 18 corn oil,
animal tissues,
bacteria
linolenic acid cis-
9-,
cis-
12-,
cis-
15-
octadecatrienoic acid
5,8,11-eicosatrienoic acid
8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid
7,10,13-docosatrienoic acid
8,11,14-docosatrienoic acid 18
20
20
22
22
animal tissues
brain tissue
phospholipids
arachidonic acid 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid
4,7,10,13-docosatetraenoic acid
4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid 20
22
22 liver, brain tissue
brain tissue
brain tissue
See as table: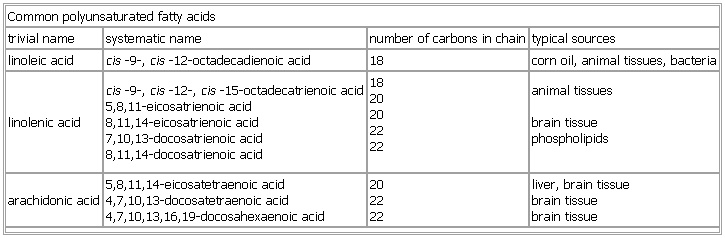
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Polyunsaturated fatty acid — Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are those which contain more than one double bond. Methylene Interrupted Polyenes These fatty acids have 2 or more cis double bonds which are separated from each other by a single methylene group. (This form is… … Wikipedia
Common fatty acids in foods — ▪ Table Common fatty acids in foods fatty acid shorthand* typical source Saturated fatty acids butyric 4:0 butterfat caproic 6:0 butterfat caprylic 8:0 coconut oil capric 10:0 coconut oil lauric 12:0 coconut oil, palm kernel oil myristic 14:0… … Universalium
Fatty acid — Not to be confused with fat. Butyric acid, a short chain fatty acid Types of fats in food Unsaturated fat Monounsaturated fat Polyun … Wikipedia
Omega-3 fatty acid — For an explanation of n and numerical nomenclature (such as n−3 or 18:3), see Fatty acid#Nomenclature. Types of fats in food Unsaturated fat Monounsaturated fat Polyunsaturated fat Trans fat Cis fat Omega fatty acids: ω−3 ω−6 ω−9 Saturated fat… … Wikipedia
Omega-6 fatty acid — For an explanation of n and numerical nomenclature (such as n−6 or 18:2), see Fatty acid#Nomenclature. Types of fats in food Unsaturated fat Monounsaturated fat Polyunsaturated fat Trans fat Cis fat Omega fatty acids: ω−3 ω−6 ω−9 Saturated fat… … Wikipedia
Essential fatty acid — Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that cannot be constructed within an organism from other components (generally all references are to humans) by any known chemical pathways; and therefore mustbe obtained from the diet. The term… … Wikipedia
Omega-9 fatty acid — For an explanation of n and numerical nomenclature (such as n−9 or 18:1), see Fatty acid#Nomenclature. Types of fats in food Unsaturated fat Monounsaturated fat Polyunsaturated fat Trans fat Cis fat Omega fatty acids: ω−3 ω−6 ω−9 Saturated fat… … Wikipedia
lipid — /lip id, luy pid/, n. Biochem. any of a group of organic compounds that are greasy to the touch, insoluble in water, and soluble in alcohol and ether: lipids comprise the fats and other esters with analogous properties and constitute, with… … Universalium
nutrition, human — Introduction process by which substances in food are transformed into body tissues and provide energy for the full range of physical and mental activities that make up human life. The study of human nutrition is interdisciplinary in… … Universalium
nutritional disease — Introduction any of the nutrient related diseases and conditions that cause illness in humans. They may include deficiencies or excesses in the diet, obesity and eating disorders, and chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease,… … Universalium

