- Important gemstones
-
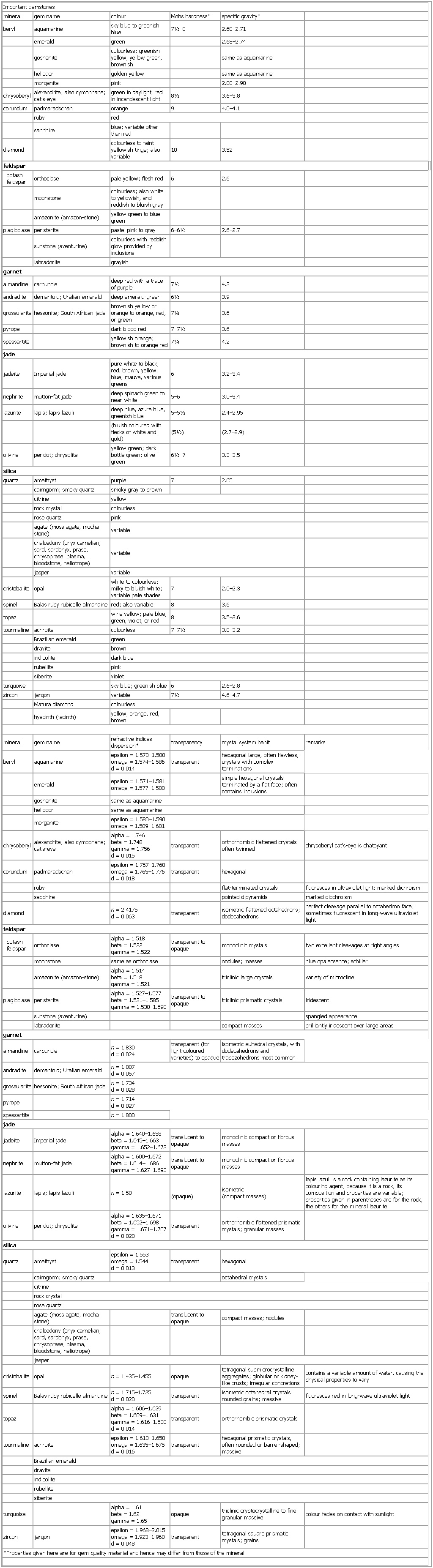
▪ TableImportant gemstonesmineral gem name colour Mohs hardness* specific gravity*beryl aquamarine sky blue to greenish blue 7½–8 2.68–2.71emerald green 2.68–2.74goshenite colourless; greenish yellow, yellow green, brownish same as aquamarineheliodor golden yellow same as aquamarinemorganite pink 2.80–2.90chrysoberyl alexandrite; also cymophane; cat's-eye green in daylight, red in incandescent light 8½ 3.6–3.8corundum padmaradschah orange 9 4.0–4.1ruby redsapphire blue; variable other than reddiamond colourless to faint yellowish tinge; also variable 10 3.52potashfeldspar orthoclase pale yellow; flesh red 6 2.6moonstone colourless; also white to yellowish, and reddish to bluish grayamazonite (amazon-stone) yellow green to blue greenplagioclase peristerite pastel pink to gray 6–6½ 2.6–2.7labradorite grayishalmandine carbuncle deep red with a trace of purple 7½ 4.3andradite demantoid; Uralian emerald deep emerald-green 6½ 3.9grossularite hessonite; South African jade brownish yellow or orange to orange, red, or green 7¼ 3.6pyrope dark blood red 7–7½ 3.6spessartite yellowish orange; brownish to orange red 7¼ 4.2jadeite Imperial jade pure white to black, red, brown, yellow, blue, mauve, various greens 6 3.2–3.4nephrite mutton-fat jade deep spinach green to near-white 5–6 3.0–3.4lazurite lapis; lapis lazuli deep blue, azure blue, greenish blue 5–5½ 2.4–2.95(bluish coloured with flecks of white and gold) (5½) (2.7–2.9)olivine peridot; chrysolite yellow green; dark bottle green; olive green 6½–7 3.3–3.5quartz amethyst purple 7 2.65cairngorm; smoky quartz smoky gray to browncitrine yellowrock crystal colourlessrose quartz pinkchalcedony (onyx carnelian, sard, sardonyx, prase, chrysoprase, plasma, bloodstone, heliotrope) variablejasper variablecristobalite opal white to colourless; milky to bluish white; variable pale shades 7 2.0–2.3spinel Balas ruby rubicelle almandine red; also variable 8 3.6topaz wine yellow; pale blue, green, violet, or red 8 3.5–3.6tourmaline achroite colourless 7–7½ 3.0–3.2Brazilian emerald greendravite brownindicolite dark bluerubellite pinksiberite violetturquoise sky blue; greenish blue 6 2.6–2.8zircon jargon variable 7½ 4.6–4.7Matura diamond colourlessmineral gem name refractive indices dispersion* transparency crystal system habit remarksberyl aquamarine epsilon = 1.570–1.580omega = 1.574–1.586d = 0.014 transparent hexagonal large, often flawless, crystals with complex terminationsemerald epsilon = 1.571–1.581omega = 1.577–1.588 simple hexagonal crystals terminated by a flat face; often contains inclusionsgoshenite same as aquamarineheliodor same as aquamarinemorganite epsilon = 1.580–1.590omega = 1.589–1.601chrysoberyl alexandrite; also cymophane; cat's-eye alpha = 1.746beta = 1.748gamma = 1.756d = 0.015 transparent orthorhombic flattened crystals often twinned chrysoberyl cat's-eye is chatoyantcorundum padmaradschah epsilon = 1.757–1.768omega = 1.765–1.776d = 0.018 transparent hexagonalruby flat-terminated crystals fluoresces in ultraviolet light; marked dichroismsapphire pointed dipyramids marked diochroismdiamond n = 2.4175d = 0.063 transparent isometric flattened octahedrons; dodecahedrons perfect cleavage parallel to octahedron face; sometimes fluorescent in long-wave ultraviolet lightpotashfeldspar orthoclase alpha = 1.518beta = 1.522gamma = 1.522 transparent to opaque monoclinic crystals two excellent cleavages at right anglesmoonstone same as orthoclase nodules; masses blue opalecsence; schilleramazonite (amazon-stone) alpha = 1.514beta = 1.518gamma = 1.521 triclinic large crystals variety of microclineplagioclase peristerite alpha = 1.527–1.577beta = 1.531–1.585gamma = 1.538–1.590 transparent to opaque triclinic prismatic crystals iridescentlabradorite compact masses brilliantly iridescent over large areasalmandine carbuncle n = 1.830d = 0.024 transparent (for light-coloured varieties) to opaque isometric euhedral crystals, with dodecahedrons and trapezohedrons most commonandradite demantoid; Uralian emerald n = 1.887d = 0.057grossularite hessonite; South African jade n = 1.734d = 0.028pyrope n = 1.714d = 0.027spessartite n = 1.800jadeite Imperial jade alpha = 1.640–1.658beta = 1.645–1.663gamma = 1.652–1.673 translucent to opaque monoclinic compact or fibrous massesnephrite mutton-fat jade alpha = 1.600–1.672beta = 1.614–1.686gamma = 1.627–1.693 translucent to opaque monoclinic compact or fibrous masseslazurite lapis; lapis lazuli n = 1.50(opaque) isometric(compact masses) lapis lazuli is a rock containing lazurite as its colouring agent; because it is a rock, its composition and properties are variable; properties given in parentheses are for the rock, the others for the mineral lazuriteolivine peridot; chrysolite alpha = 1.635–1.671beta = 1.652–1.698gamma = 1.671–1.707d = 0.020 transparent orthorhombic flattened prismatic crystals; granular massesquartz amethyst epsilon = 1.553omega = 1.544d = 0.013 transparent hexagonalcairngorm; smoky quartz octahedral crystalscitrinerock crystalrose quartzjaspercristobalite opal n = 1.435–1.455 opaque tetragonal submicrocrystalline aggregates; globular or kidney-like crusts; irregular concretions contains a variable amount of water, causing the physical properties to varyspinel Balas ruby rubicelle almandine n = 1.715–1.725d = 0.020 transparent isometric octahedral crystals; rounded grains; massive fluoresces red in long-wave ultraviolet lighttopaz alpha = 1.606–1.629beta = 1.609–1.631gamma = 1.616–1.638d = 0.014 transparent orthorhombic prismatic crystalstourmaline achroite epsilon = 1.610–1.650omega = 1.635–1.675d = 0.016 transparent hexagonal prismatic crystals, often rounded or barrel-shaped; massiveBrazilian emeralddraviteindicoliterubellitesiberiteturquoise alpha = 1.61beta = 1.62gamma = 1.65 opaque triclinic cryptocrystalline to fine granular massive colour fades on contact with sunlightzircon jargon epsilon = 1.968–2.015omega = 1.923–1.960d = 0.048 transparent tetragonal square prismatic crystals; grains*Properties given here are for gem-quality material and hence may differ from those of the mineral.See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
