Attenuation of sound in selected fluids
- Attenuation of sound in selected fluids
-
Attenuation of sound in selected fluids
fluid attenuation coefficient
helium 52.5
hydrogen 16.9
nitrogen 133.0
oxygen 165.0
air 137.0
carbon dioxide 140.0
water, at 0 °C (32 °F) 0.569
water, at 20 °C (68 °F) 0.253
water, at 80 °C (176 °F) 0.079
mercury, at 25 °C (77 °F) 0.057
methyl alcohol, at 30 °C (86 °F) 0.302
See as table: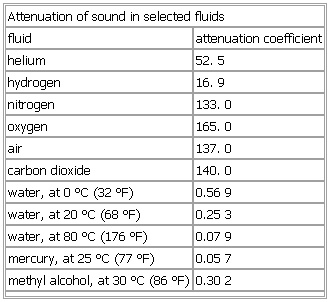
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
sound — sound1 soundable, adj. /sownd/, n. 1. the sensation produced by stimulation of the organs of hearing by vibrations transmitted through the air or other medium. 2. mechanical vibrations transmitted through an elastic medium, traveling in air at a… … Universalium
Sound — /sownd/, n. The, a strait between SW Sweden and Zealand, connecting the Kattegat and the Baltic. 87 mi. (140 km) long; 3 30 mi. (5 48 km) wide. Swedish and Danish, Oresund. * * * I Mechanical disturbance that propagates as a longitudinal wave… … Universalium
Viscosity — For other uses, see Viscosity (disambiguation). Viscosity The substance above has lower viscosity than the substance below SI symbol: μ, η SI unit: Pa·s … Wikipedia
Magnetic resonance imaging — MRI redirects here. For other meanings of MRI or Mri, see MRI (disambiguation). Magnetic resonance imaging Intervention Sagittal MR image of the knee ICD 10 PCS B?3?ZZZ … Wikipedia
Lamb waves — propagate in solid plates. They are elastic waves whose particle motion lies in the plane defined by the plate normal and the direction of wave propagation. In 1917, the English mathematician Horace Lamb published his classic analysis and… … Wikipedia

