- Representative poisonous plants
-
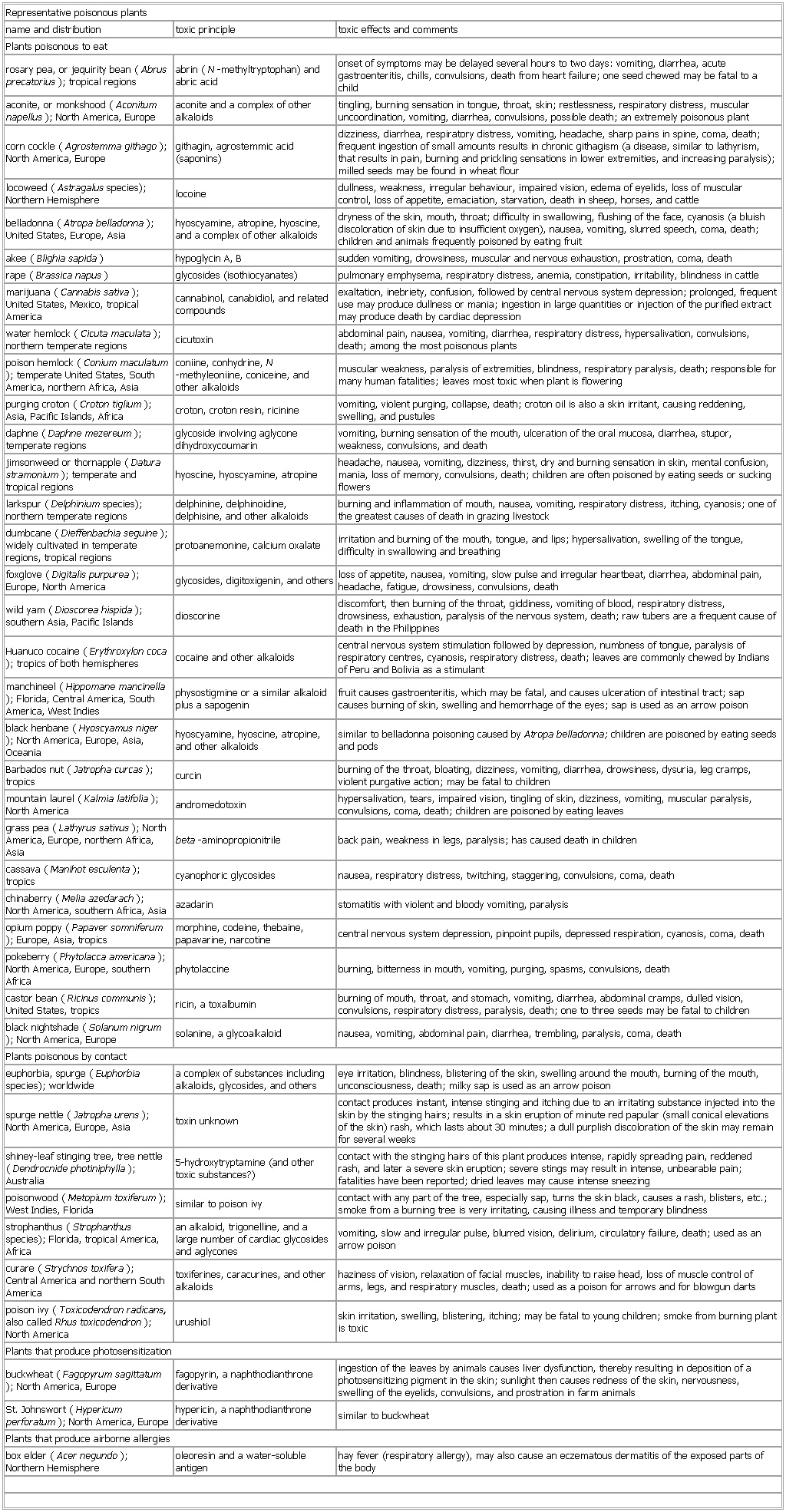
▪ TableRepresentative poisonous plantsname and distribution toxic principle toxic effects and commentsPlants poisonous to eatrosary pea, or jequirity bean (Abrus precatorius); tropical regions abrin (N-methyltryptophan) and abric acid onset of symptoms may be delayed several hours to two days: vomiting, diarrhea, acute gastroenteritis, chills, convulsions, death from heart failure; one seed chewed may be fatal to a childaconite, or monkshood (Aconitum napellus); North America, Europe aconite and a complex of other alkaloids tingling, burning sensation in tongue, throat, skin; restlessness, respiratory distress, muscular uncoordination, vomiting, diarrhea, convulsions, possible death; an extremely poisonous plantcorn cockle (Agrostemma githago); North America, Europe githagin, agrostemmic acid (saponins) dizziness, diarrhea, respiratory distress, vomiting, headache, sharp pains in spine, coma, death; frequent ingestion of small amounts results in chronic githagism (a disease, similar to lathyrism, that results in pain, burning and prickling sensations in lower extremities, and increasing paralysis); milled seeds may be found in wheat flourlocoweed (Astragalus species); Northern Hemisphere locoine dullness, weakness, irregular behaviour, impaired vision, edema of eyelids, loss of muscular control, loss of appetite, emaciation, starvation, death in sheep, horses, and cattlebelladonna (Atropa belladonna); United States, Europe, Asia hyoscyamine, atropine, hyoscine, and a complex of other alkaloids dryness of the skin, mouth, throat; difficulty in swallowing, flushing of the face, cyanosis (a bluish discoloration of skin due to insufficient oxygen), nausea, vomiting, slurred speech, coma, death; children and animals frequently poisoned by eating fruitakee (Blighia sapida) hypoglycin A, B sudden vomiting, drowsiness, muscular and nervous exhaustion, prostration, coma, deathrape (Brassica napus) glycosides (isothiocyanates) pulmonary emphysema, respiratory distress, anemia, constipation, irritability, blindness in cattlemarijuana (Cannabis sativa); United States, Mexico, tropical America cannabinol, canabidiol, and related compounds exaltation, inebriety, confusion, followed by central nervous system depression; prolonged, frequent use may produce dullness or mania; ingestion in large quantities or injection of the purified extract may produce death by cardiac depressionwater hemlock (Cicuta maculata); northern temperate regions cicutoxin abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, respiratory distress, hypersalivation, convulsions, death; among the most poisonous plantspoison hemlock (Conium maculatum); temperate United States, South America, northern Africa, Asia coniine, conhydrine, N-methyleoniine, coniceine, and other alkaloids muscular weakness, paralysis of extremities, blindness, respiratory paralysis, death; responsible for many human fatalities; leaves most toxic when plant is floweringpurging croton (Croton tiglium); Asia, Pacific Islands, Africa croton, croton resin, ricinine vomiting, violent purging, collapse, death; croton oil is also a skin irritant, causing reddening, swelling, and pustulesdaphne (Daphne mezereum); temperate regions glycoside involving aglycone dihydroxycoumarin vomiting, burning sensation of the mouth, ulceration of the oral mucosa, diarrhea, stupor, weakness, convulsions, and deathjimsonweed or thornapple (Datura stramonium); temperate and tropical regions hyoscine, hyoscyamine, atropine headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, thirst, dry and burning sensation in skin, mental confusion, mania, loss of memory, convulsions, death; children are often poisoned by eating seeds or sucking flowerslarkspur (Delphinium species); northern temperate regions delphinine, delphinoidine, delphisine, and other alkaloids burning and inflammation of mouth, nausea, vomiting, respiratory distress, itching, cyanosis; one of the greatest causes of death in grazing livestockdumbcane (Dieffenbachia seguine); widely cultivated in temperate regions, tropical regions protoanemonine, calcium oxalate irritation and burning of the mouth, tongue, and lips; hypersalivation, swelling of the tongue, difficulty in swallowing and breathingfoxglove (Digitalis purpurea); Europe, North America glycosides, digitoxigenin, and others loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, slow pulse and irregular heartbeat, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, fatigue, drowsiness, convulsions, deathwild yam (Dioscorea hispida); southern Asia, Pacific Islands dioscorine discomfort, then burning of the throat, giddiness, vomiting of blood, respiratory distress, drowsiness, exhaustion, paralysis of the nervous system, death; raw tubers are a frequent cause of death in the PhilippinesHuanuco cocaine (Erythroxylon coca); tropics of both hemispheres cocaine and other alkaloids central nervous system stimulation followed by depression, numbness of tongue, paralysis of respiratory centres, cyanosis, respiratory distress, death; leaves are commonly chewed by Indians of Peru and Bolivia as a stimulantmanchineel (Hippomane mancinella); Florida, Central America, South America, West Indies physostigmine or a similar alkaloid plus a sapogenin fruit causes gastroenteritis, which may be fatal, and causes ulceration of intestinal tract; sap causes burning of skin, swelling and hemorrhage of the eyes; sap is used as an arrow poisonblack henbane (Hyoscyamus niger); North America, Europe, Asia, Oceania hyoscyamine, hyoscine, atropine, and other alkaloids similar to belladonna poisoning caused by Atropa belladonna; children are poisoned by eating seeds and podsBarbados nut (Jatropha curcas); tropics curcin burning of the throat, bloating, dizziness, vomiting, diarrhea, drowsiness, dysuria, leg cramps, violent purgative action; may be fatal to childrenmountain laurel (Kalmia latifolia); North America andromedotoxin hypersalivation, tears, impaired vision, tingling of skin, dizziness, vomiting, muscular paralysis, convulsions, coma, death; children are poisoned by eating leavesgrass pea (Lathyrus sativus); North America, Europe, northern Africa, Asia beta-aminopropionitrile back pain, weakness in legs, paralysis; has caused death in childrencassava (Manihot esculenta); tropics cyanophoric glycosides nausea, respiratory distress, twitching, staggering, convulsions, coma, deathchinaberry (Melia azedarach); North America, southern Africa, Asia azadarin stomatitis with violent and bloody vomiting, paralysisopium poppy (Papaver somniferum); Europe, Asia, tropics morphine, codeine, thebaine, papavarine, narcotine central nervous system depression, pinpoint pupils, depressed respiration, cyanosis, coma, deathpokeberry (Phytolacca americana); North America, Europe, southern Africa phytolaccine burning, bitterness in mouth, vomiting, purging, spasms, convulsions, deathcastor bean (Ricinus communis); United States, tropics ricin, a toxalbumin burning of mouth, throat, and stomach, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, dulled vision, convulsions, respiratory distress, paralysis, death; one to three seeds may be fatal to childrenblack nightshade (Solanum nigrum); North America, Europe solanine, a glycoalkaloid nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, trembling, paralysis, coma, deathPlants poisonous by contacteuphorbia, spurge (Euphorbia species); worldwide a complex of substances including alkaloids, glycosides, and others eye irritation, blindness, blistering of the skin, swelling around the mouth, burning of the mouth, unconsciousness, death; milky sap is used as an arrow poisonspurge nettle (Jatropha urens); North America, Europe, Asia toxin unknown contact produces instant, intense stinging and itching due to an irritating substance injected into the skin by the stinging hairs; results in a skin eruption of minute red papular (small conical elevations of the skin) rash, which lasts about 30 minutes; a dull purplish discoloration of the skin may remain for several weeksshiney-leaf stinging tree, tree nettle (Dendrocnide photiniphylla); Australia 5-hydroxytryptamine (and other toxic substances?) contact with the stinging hairs of this plant produces intense, rapidly spreading pain, reddened rash, and later a severe skin eruption; severe stings may result in intense, unbearable pain; fatalities have been reported; dried leaves may cause intense sneezingpoisonwood (Metopium toxiferum); West Indies, Florida similar to poison ivy contact with any part of the tree, especially sap, turns the skin black, causes a rash, blisters, etc.; smoke from a burning tree is very irritating, causing illness and temporary blindnessstrophanthus (Strophanthus species); Florida, tropical America, Africa an alkaloid, trigonelline, and a large number of cardiac glycosides and aglycones vomiting, slow and irregular pulse, blurred vision, delirium, circulatory failure, death; used as an arrow poisoncurare (Strychnos toxifera); Central America and northern South America toxiferines, caracurines, and other alkaloids haziness of vision, relaxation of facial muscles, inability to raise head, loss of muscle control of arms, legs, and respiratory muscles, death; used as a poison for arrows and for blowgun dartspoison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans, also called Rhus toxicodendron); North America urushiol skin irritation, swelling, blistering, itching; may be fatal to young children; smoke from burning plant is toxicPlants that produce photosensitizationbuckwheat (Fagopyrum sagittatum); North America, Europe fagopyrin, a naphthodianthrone derivative ingestion of the leaves by animals causes liver dysfunction, thereby resulting in deposition of a photosensitizing pigment in the skin; sunlight then causes redness of the skin, nervousness, swelling of the eyelids, convulsions, and prostration in farm animalsSt. Johnswort (Hypericum perforatum); North America, Europe hypericin, a naphthodianthrone derivative similar to buckwheatPlants that produce airborne allergiesbox elder (Acer negundo); Northern Hemisphere oleoresin and a water-soluble antigen hay fever (respiratory allergy), may also cause an eczematous dermatitis of the exposed parts of the bodySee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
