Nutrient composition of red meats
- Nutrient composition of red meats
-
Nutrient composition of red meats (per 100 g)
meat type and cut energy (
kcal) water
(g) protein
(g) fat
(g) cholesterol (
mg) vitamin B
12(μg) thiamin
Beef
chuck arm
pot roast 219 58 33.02 8.70 101 3.40 0.080 3.79 8.66
rib eye steak 225 59 28.04 11.70 80 3.32 0.100 2.57 6.99
short ribs 295 50 30.76 18.13 93 3.46 0.065 3.36 7.80
tenderloin 212 60 28.25 10.10 84 2.57 0.130 3.58 5.59
top sirloin 200 61 30.37 7.80 89 2.85 0.130 3.36 6.52
ground
(extra lean) 265 54 28.58 15.80 99 2.56 0.070 2.77 6.43
Pork
loin roast 169 62 30.24 7.21 78 0.55 0.639 1.06 2.31
tenderloin 164 66 8.14 4.81 79 0.55 0.940 1.47 2.63
Boston
shoulder roast 232 61 24.21 14.30 85 0.93 0.669 1.56 4.23
spareribs 397 40 29.06 30.30 121 1.08 0.382 1.85 4.60
cured ham
(extra lean) 145 68 20.93 5.53 53 0.65 0.754 1.48 2.88
Lamb
leg roast 191 64 28.30 7.74 89 2.64 0.110 2.12 4.94
loin chop 202 63 26.59 9.76 87 2.16 0.100 2.44 4.06
blade chop 209 63 24.61 11.57 87 2.74 0.090 2.07 6.48
Veal
loin chop 175 65 26.32 6.94 106 1.31 0.060 0.85 3.24
rib chop 177 65 25.76 7.44 115 1.58 0.060 0.96 4.49
Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Composition of Foods, Agriculture Handbook no. 8-10, 8-13, and 8-17.
See as table: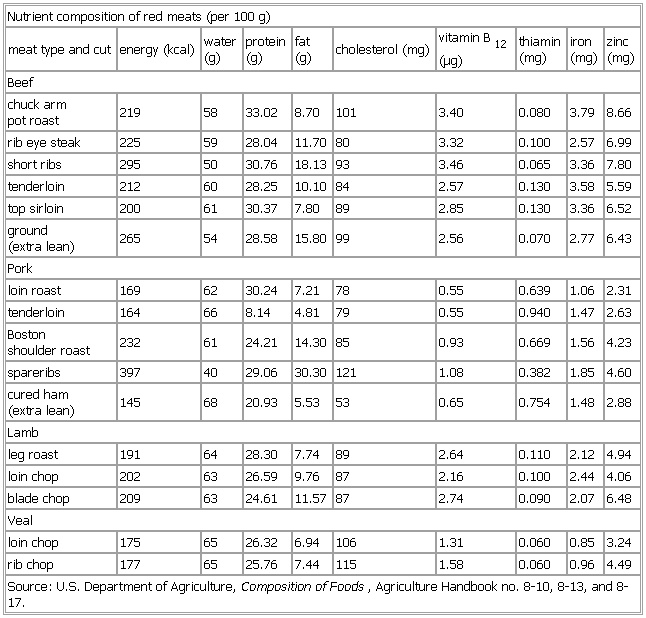
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
meat processing — Introduction preparation of meat for human consumption. Meat is the common term used to describe the edible portion of animal tissues and any processed or manufactured products prepared from these tissues. Meats are often classified… … Universalium
nutrition, human — Introduction process by which substances in food are transformed into body tissues and provide energy for the full range of physical and mental activities that make up human life. The study of human nutrition is interdisciplinary in… … Universalium
Human nutrition — For aspects of nutrition science not specific to humans, see Nutrition. Human nutrition is the provision to humans to obtain the materials necessary to support life. In general, humans can survive for two to eight weeks without food, depending on … Wikipedia
food preservation — Any method by which food is protected against spoilage by oxidation, bacteria, molds, and microorganisms. Traditional methods include dehydration, smoking, salting, controlled fermentation (including pickling), and candying; certain spices have… … Universalium
poultry processing — Introduction preparation of meat from various types of fowl (poultry) for consumption by humans. Poultry is a major source of consumable animal protein. For example, per capita consumption of poultry in the United States has more than … Universalium
Omega-3 fatty acid — For an explanation of n and numerical nomenclature (such as n−3 or 18:3), see Fatty acid#Nomenclature. Types of fats in food Unsaturated fat Monounsaturated fat Polyunsaturated fat Trans fat Cis fat Omega fatty acids: ω−3 ω−6 ω−9 Saturated fat… … Wikipedia
Shellfish Association of Great Britain — The Shellfish Association of Great Britain (SAGB) is a historic association that was founded as the Oyster Merchants’ and Planters’ Association in 1903, it was renamed the SAGB in 1969. They cover a wide range of topics within the shellfish… … Wikipedia
Zinc — This article is about the metallic element. For other uses, see Zinc (disambiguation). copper ← zinc → gallium ↑ Zn ↓ Cd … Wikipedia
Nutrition — The Nutrition Facts table indicates the amounts of nutrients which experts recommend to limit or consume in adequate amounts. Nutrition (also called nourishment or aliment) is the provision, to cells and organisms, of the materials necessary (in… … Wikipedia
Egg (food) — Chicken egg redirects here. For the causality dilemma, see Chicken or the egg. On the left a chicken egg, the egg most commonly e … Wikipedia

