- Melting (in bold) and boiling points (C) of heteroaromatic compounds
-
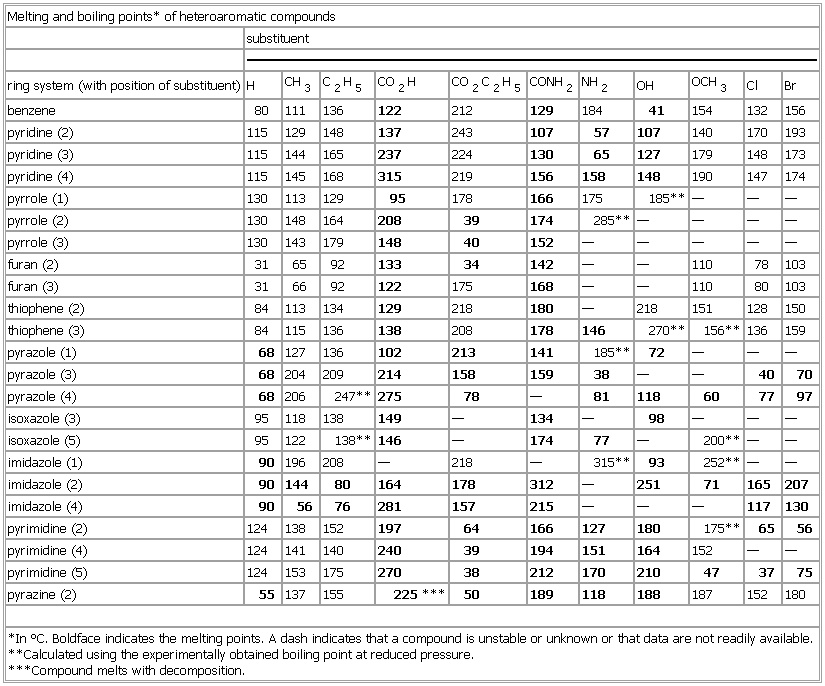
▪ TableMelting and boiling points* of heteroaromatic compoundssubstituentring system (with position of substituent) H CH3 C2H5 CO2H CO2C2H5 CONH2 NH2 OH OCH3 Cl Brbenzene 80 111 136 122 212 129 184 41 154 132 156pyridine (2) 115 129 148 137 243 107 57 107 140 170 193pyridine (3) 115 144 165 237 224 130 65 127 179 148 173pyridine (4) 115 145 168 315 219 156 158 148 190 147 174pyrrole (1) 130 113 129 95 178 166 175 185** — — —pyrrole (2) 130 148 164 208 39 174 285** — — — —pyrrole (3) 130 143 179 148 40 152 — — — — —furan (2) 31 65 92 133 34 142 — — 110 78 103furan (3) 31 66 92 122 175 168 — — 110 80 103thiophene (2) 84 113 134 129 218 180 — 218 151 128 150thiophene (3) 84 115 136 138 208 178 146 270** 156** 136 159pyrazole (1) 68 127 136 102 213 141 185** 72 — — —pyrazole (3) 68 204 209 214 158 159 38 — — 40 70pyrazole (4) 68 206 247** 275 78 — 81 118 60 77 97isoxazole (3) 95 118 138 149 — 134 — 98 — — —isoxazole (5) 95 122 138** 146 — 174 77 — 200** — —imidazole (1) 90 196 208 — 218 — 315** 93 252** — —imidazole (2) 90 144 80 164 178 312 — 251 71 165 207imidazole (4) 90 56 76 281 157 215 — — — 117 130pyrimidine (2) 124 138 152 197 64 166 127 180 175** 65 56pyrimidine (4) 124 141 140 240 39 194 151 164 152 — —pyrimidine (5) 124 153 175 270 38 212 170 210 47 37 75pyrazine (2) 55 137 155 225*** 50 189 118 188 187 152 180*In °C. Boldface indicates the melting points. A dash indicates that a compound is unstable or unknown or that data are not readily available.**Calculated using the experimentally obtained boiling point at reduced pressure.***Compound melts with decomposition.See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
