- Antibiotics
-
▪ TableAntibioticsdrug class andgeneric namecommon trade name(s) common use(s)aminoglycosides (inhibit protein synthesis)gentamicin Garamycin infections of the respiratory and urinary tracts, blood, abdominal cavity; pelvic inflammatory diseasetobramycin AKTob, Nebcin infections of the respiratory and urinary tracts, blood, abdominal cavity; pelvic imflammatory diseasecephalosporins () (inhibit cell wall synthesis)cefaclor Ceclor infections of the respiratory and urinary tracts and skin; otitis mediacefamandole Mandol infections of the respiratory and urinary tracts, skin, bone and joints, and blood; peritonitiscefazolin Ancef, Kefzol infections of the respiratory and genitourinary tracts, skin, bone and joints, and blood; endocarditisceftriaxone Rocephin infections of the respiratory and urinary tracts, skin, blood, abdominal cavity, and bone and joints; pelvic inflammatory disease; gonorrhea; meningitiscefuroxime Ceftin, Kefurox infections of the respiratory and urinary tracts, skin, bone and joints, and bloodcephalexin Biocef, Keflex infections of the respiratory and urinary tracts, skin, and bone; otitis mediachloramphenicols (inhibit protein synthesis)chloramphenicol () Chloromycetin infections of the eyes, ears, and skin; cystic fibrosis; prevention of infection in minor woundsfluoroquinolones (interfere with DNA synthesis)ciprofloxacin Cipro infections of the respiratory and urinary tracts, skin, eyes, abdominal cavity, and bone and joints; diarrhea; gonorrhea; sinusitis; pneumonia; prostatitis; anthraxnorfloxacin Chibroxin, Noroxin urinary tract infections, STDs caused by N. gonorrhoeae, eye infections, prostatitislincosamides (inhibit protein systhesis)clindamycin Cleocin infections of the respiratory tract, skin, and abdominal cavity; acne; pelvic inflammatory diseasemacrolides (inhibit protein synthesis)azithromycin Zithromax infections of the respiratory tract and skin; STDs; otitis media; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; pneumoniaclarithromycin Biaxin infections of the respiratory tract and skin; otitis mediaerythromycin () E.E.S., E-mycin, Eryc infections of the respiratory tract, skin, and eyes; STDs; pertussis; diptheria; intestinal amebiasis; otitis media; acne; Legionnaire disease; prevention of infection in minor woundsnitrofurans (inactivate essential cell components)nitrofurantoin Furadantin, Macrobid urinary tract infectionsamoxicillin Amoxil, Trimox various streptococcal and staphylococcal infectionsampicillin () Marcillin, Omnipen infections of the respiratory and urinary tract and blood; meningitis; gonococcal infections; endocarditispenicillin G Bicillin, Pen-G Pot, Wycillinvarious streptococcal and staphylococcal infectionspiperacillin Pipracil infections of the respiratory and genitourinary tracts, skin, abdominal cavity, bone and joints, and bloodticarcillin Ticar infections of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts; streptococcal and pseudomonas infections; gonorrhea; tonsillitis; Lyme disease; impetigo; otitis media; meningitistetracycline Achromycin, Sumycin rickettsia, pneumonia, chlamydia, intestinal amebiasis, acne, prevention of infection in minor woundsmiscellaneous antibioticsaztreonam Azactam infections of the respiratory and genitourinary tracts, skin, abdominal cavity, and bloodimipenem-cilistatin Primaxin infections of the respiratory and genitourinary tracts, skin, abdominal cavity, bone and joints, and blood; endocarditismetronidazole Flagyl, Protostat infections of the vagina and gastrointestinal tractrifampin Rifadin, Rimactane tuberculosistrimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole Bactrim, Cotrim, Septra urinary tract infections, shigellosis, otitis media, bronchitis, traveler's diarrheavancomycin Lyphocin, Vancocin infections resistant to penicillins and cephalosporinsSee as table:
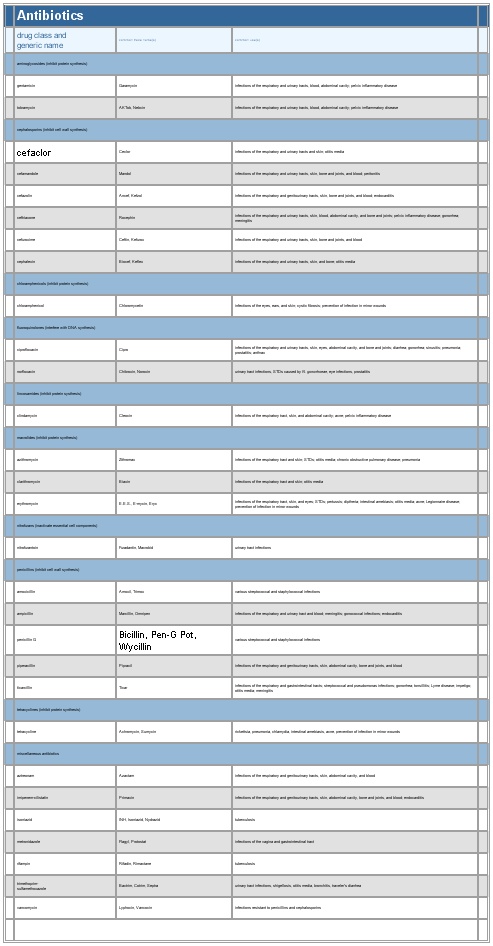 See as table:
See as table: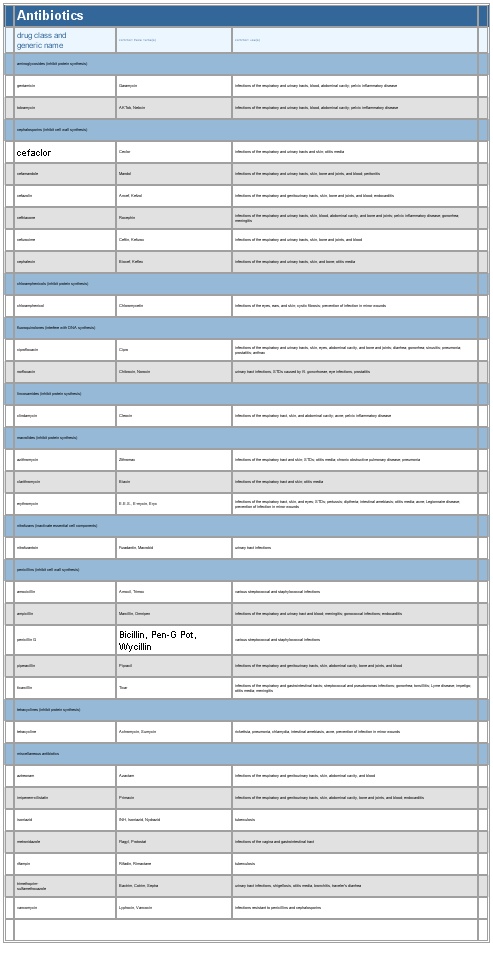
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
