- Launch vehicles
-
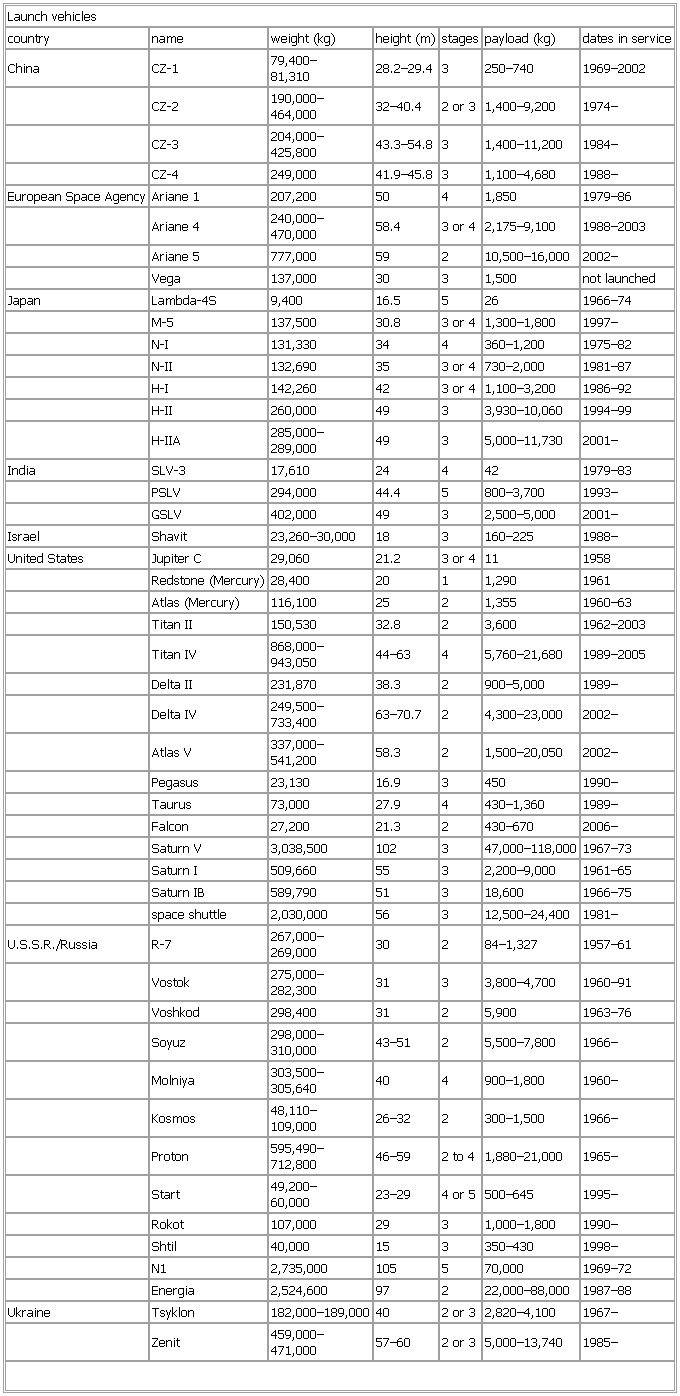
▪ TableLaunch vehiclesChina CZ-1 79,400–81,310 28.2–29.4 3 250–740 1969–2002CZ-2 190,000–464,000 32–40.4 2 or 3 1,400–9,200 1974–CZ-3 204,000–425,800 43.3–54.8 3 1,400–11,200 1984–CZ-4 249,000 41.9–45.8 3 1,100–4,680 1988–Ariane 4 240,000–470,000 58.4 3 or 4 2,175–9,100 1988–2003Ariane 5 777,000 59 2 10,500–16,000 2002–Vega 137,000 30 3 1,500 not launchedJapan Lambda-4S 9,400 16.5 5 26 1966–74M-5 137,500 30.8 3 or 4 1,300–1,800 1997–N-I 131,330 34 4 360–1,200 1975–82N-II 132,690 35 3 or 4 730–2,000 1981–87H-I 142,260 42 3 or 4 1,100–3,200 1986–92H-II 260,000 49 3 3,930–10,060 1994–99H-IIA 285,000–289,000 49 3 5,000–11,730 2001–India SLV-3 17,610 24 4 42 1979–83PSLV 294,000 44.4 5 800–3,700 1993–GSLV 402,000 49 3 2,500–5,000 2001–Israel Shavit 23,260–30,000 18 3 160–225 1988–United States Jupiter C 29,060 21.2 3 or 4 11 1958Titan IV 868,000–943,050 44–63 4 5,760–21,680 1989–2005Delta IV 249,500–733,400 63–70.7 2 4,300–23,000 2002–Atlas V 337,000–541,200 58.3 2 1,500–20,050 2002–Pegasus 23,130 16.9 3 450 1990–Taurus 73,000 27.9 4 430–1,360 1989–Falcon 27,200 21.3 2 430–670 2006–Saturn I 509,660 55 3 2,200–9,000 1961–65Saturn IB 589,790 51 3 18,600 1966–75U.S.S.R./Russia R-7 267,000–269,000 30 2 84–1,327 1957–61Vostok 275,000–282,300 31 3 3,800–4,700 1960–91Voshkod 298,400 31 2 5,900 1963–76Soyuz 298,000–310,000 43–51 2 5,500–7,800 1966–Molniya 303,500–305,640 40 4 900–1,800 1960–Kosmos 48,110–109,000 26–32 2 300–1,500 1966–712,800 46–59 2 to 4 1,880–21,000 1965–Start 49,200–60,000 23–29 4 or 5 500–645 1995–Rokot 107,000 29 3 1,000–1,800 1990–Shtil 40,000 15 3 350–430 1998–N1 2,735,000 105 5 70,000 1969–72Energia 2,524,600 97 2 22,000–88,000 1987–88Ukraine Tsyklon 182,000–189,000 40 2 or 3 2,820–4,100 1967–Zenit 459,000–471,000 57–60 2 or 3 5,000–13,740 1985–See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
