- Examples of noninfectious diseases of animals
-
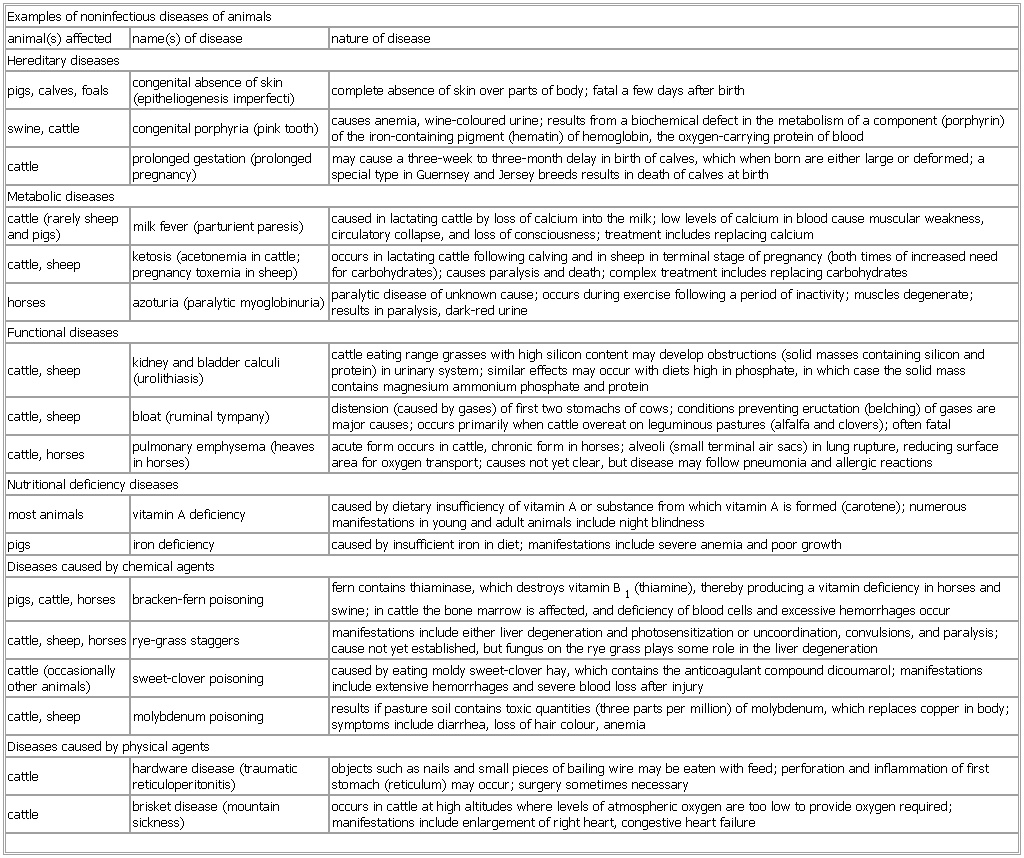
▪ TableExamples of noninfectious diseases of animalsanimal(s) affected name(s) of disease nature of diseaseHereditary diseasespigs, calves, foals congenital absence of skin (epitheliogenesis imperfecti) complete absence of skin over parts of body; fatal a few days after birthswine, cattle congenital porphyria (pink tooth) causes anemia, wine-coloured urine; results from a biochemical defect in the metabolism of a component (porphyrin) of the iron-containing pigment (hematin) of hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein of bloodcattle prolonged gestation (prolonged pregnancy) may cause a three-week to three-month delay in birth of calves, which when born are either large or deformed; a special type in Guernsey and Jersey breeds results in death of calves at birthMetabolic diseasescattle (rarely sheep and pigs) milk fever (parturient paresis) caused in lactating cattle by loss of calcium into the milk; low levels of calcium in blood cause muscular weakness, circulatory collapse, and loss of consciousness; treatment includes replacing calciumcattle, sheep ketosis (acetonemia in cattle; pregnancy toxemia in sheep) occurs in lactating cattle following calving and in sheep in terminal stage of pregnancy (both times of increased need for carbohydrates); causes paralysis and death; complex treatment includes replacing carbohydrateshorses azoturia (paralytic myoglobinuria) paralytic disease of unknown cause; occurs during exercise following a period of inactivity; muscles degenerate; results in paralysis, dark-red urineFunctional diseasescattle, sheep kidney and bladder calculi (urolithiasis) cattle eating range grasses with high silicon content may develop obstructions (solid masses containing silicon and protein) in urinary system; similar effects may occur with diets high in phosphate, in which case the solid mass contains magnesium ammonium phosphate and proteincattle, sheep bloat (ruminal tympany) distension (caused by gases) of first two stomachs of cows; conditions preventing eructation (belching) of gases are major causes; occurs primarily when cattle overeat on leguminous pastures (alfalfa and clovers); often fatalcattle, horses pulmonary emphysema (heaves in horses) acute form occurs in cattle, chronic form in horses; alveoli (small terminal air sacs) in lung rupture, reducing surface area for oxygen transport; causes not yet clear, but disease may follow pneumonia and allergic reactionsNutritional deficiency diseasesmost animals vitamin A deficiency caused by dietary insufficiency of vitamin A or substance from which vitamin A is formed (carotene); numerous manifestations in young and adult animals include night blindnesspigs iron deficiency caused by insufficient iron in diet; manifestations include severe anemia and poor growthDiseases caused by chemical agentspigs, cattle, horses bracken-fern poisoning fern contains thiaminase, which destroys vitamin B1 (thiamine), thereby producing a vitamin deficiency in horses and swine; in cattle the bone marrow is affected, and deficiency of blood cells and excessive hemorrhages occurcattle, sheep, horses rye-grass staggers manifestations include either liver degeneration and photosensitization or uncoordination, convulsions, and paralysis; cause not yet established, but fungus on the rye grass plays some role in the liver degenerationcattle (occasionally other animals) sweet-clover poisoning caused by eating moldy sweet-clover hay, which contains the anticoagulant compound dicoumarol; manifestations include extensive hemorrhages and severe blood loss after injurycattle, sheep molybdenum poisoning results if pasture soil contains toxic quantities (three parts per million) of molybdenum, which replaces copper in body; symptoms include diarrhea, loss of hair colour, anemiaDiseases caused by physical agentscattle hardware disease (traumatic reticuloperitonitis) objects such as nails and small pieces of bailing wire may be eaten with feed; perforation and inflammation of first stomach (reticulum) may occur; surgery sometimes necessarycattle brisket disease (mountain sickness) occurs in cattle at high altitudes where levels of atmospheric oxygen are too low to provide oxygen required; manifestations include enlargement of right heart, congestive heart failureSee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
