Relative abundances of the elements
- Relative abundances of the elements
-
Relative abundances of the elements
*0 percent here stands for any quantity less than 10–6 percent.
See as table: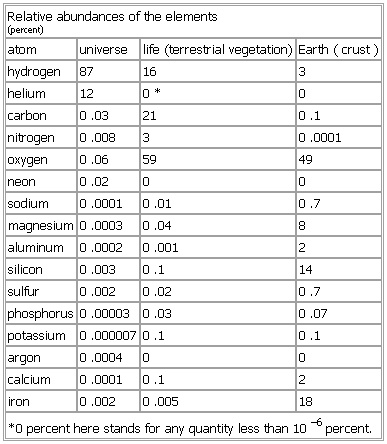
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Abundance of the chemical elements — Estimated proportions of matter, dark matter and dark energy in the universe. Only the fraction of the mass and energy in the universe labeled atoms is composed of chemical elements. The abundance of a chemical element measures how relatively… … Wikipedia
Gas giant — A gas giant (sometimes also known as a Jovian planet after the planet Jupiter, or giant planet) is a large planet that is not primarily composed of rock or other solid matter. There are four gas giants in our Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus … Wikipedia
Stellar nucleosynthesis — is the collective term for the nuclear reactions taking place in stars to build the nuclei of the heavier elements. (For other such processes, see nucleosynthesis.)The processes involved began to be understood early in the twentieth century, when … Wikipedia
Urey, Harold C(layton) — born April 29, 1893, Walkerton, Ind., U.S. died Jan. 5, 1981, La Jolla, Calif. U.S. scientist. He received his doctorate from the University of California at Berkeley and thereafter taught at various universities. He was awarded a Nobel Prize in… … Universalium
solar system — the sun together with all the planets and other bodies that revolve around it. [1695 1705] * * * The Sun, its planets, and the small bodies (see asteroid, Centaur object, comet, Kuiper belt, meteorite, and Oort cloud) interplanetary dust and gas… … Universalium
chemical element — Introduction also called element, any substance that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by ordinary chemical processes. Elements are the fundamental materials of which all matter is composed. This article considers the… … Universalium
Sun — This article is about the star. For other uses, see Sun (disambiguation). The Sun … Wikipedia
Big Bang nucleosynthesis — In physical cosmology, Big Bang nucleosynthesis (or primordial nucleosynthesis) refers to the production of nuclei other than those of H 1 (i.e. the normal, light isotope of hydrogen, whose nuclei consist of a single proton each) during the early … Wikipedia
meteorite — meteoritic /mee tee euh rit ik/, meteoritical, meteorital /mee tee euh ruyt l/, adj. /mee tee euh ruyt /, n. 1. a mass of stone or metal that has reached the earth from outer space; a fallen meteoroid. 2. a meteoroid. [1815 25; METEOR + ITE1] * * … Universalium
atmosphere, evolution of — Introduction the development of Earth s (Earth) atmosphere across geologic time. The process by which the current atmosphere arose from earlier conditions is complex; however, evidence related to the evolution of Earth s atmosphere, though… … Universalium

