FAO Soil Classification System
- FAO Soil Classification System
-
Soil classification system of the Food and Agriculture Organization
soil group abbrevi-
ation defining
characteristics name
derivation percent
of Earth's
land area
See as table:
Soils defined by parent material
"to turn") 2.67
Soils defined by topography
mass") 5.74
thin soil
rhegos (
Greek: "blanket") 2.07
Soils defined by climate, organisms, and time
accumulation
sol etz (
Russian: "strongly salty") 1.08
Kastanozem KS warm, dry steppe environment
castanea zemlja (Latin-Russian: "chestnut earth") 3.71
Phaeozem PH warm, wet steppe environment
phaios zemlja (Greek-Russian: "dusky earth") 1.51
humid tropics
acer (
Latin: "strong acid") 7.97
and warm
temperate areas
alumen (
Latin: "aluminum") 0.80
weathered; humid tropics
ferrum alumen (
Latin: "iron-
aluminum") 5.98
tropics
lixivia (
Latin: "washing") 3.47
Nitisol NT extensive clay migration; tropics
nitidus (
Latin: "shiny") 1.59
table; plinthite
plinthos (
Greek: "brick") 0.48
Luvisol LV clay accumulation; distinct seasons
luere (
Latin: "to wash") 5.18
iron and aluminum oxides and humus
pod zola (
Russian: "under ash") 3.87
area; bleached
horizon over
clayey horizon
albus (
Latin: "white") 2.55
and thawing; waterlogged
during thaw; permafrost within
1 metre (3 feet) of
the land surface
kryros (
Greek: "cold") —
Anthrosol AT extensive human modification
anthropos (
Greek: "man") 0.004
formation; recent
cambiare (
Latin: "to change") 11.96
See as table: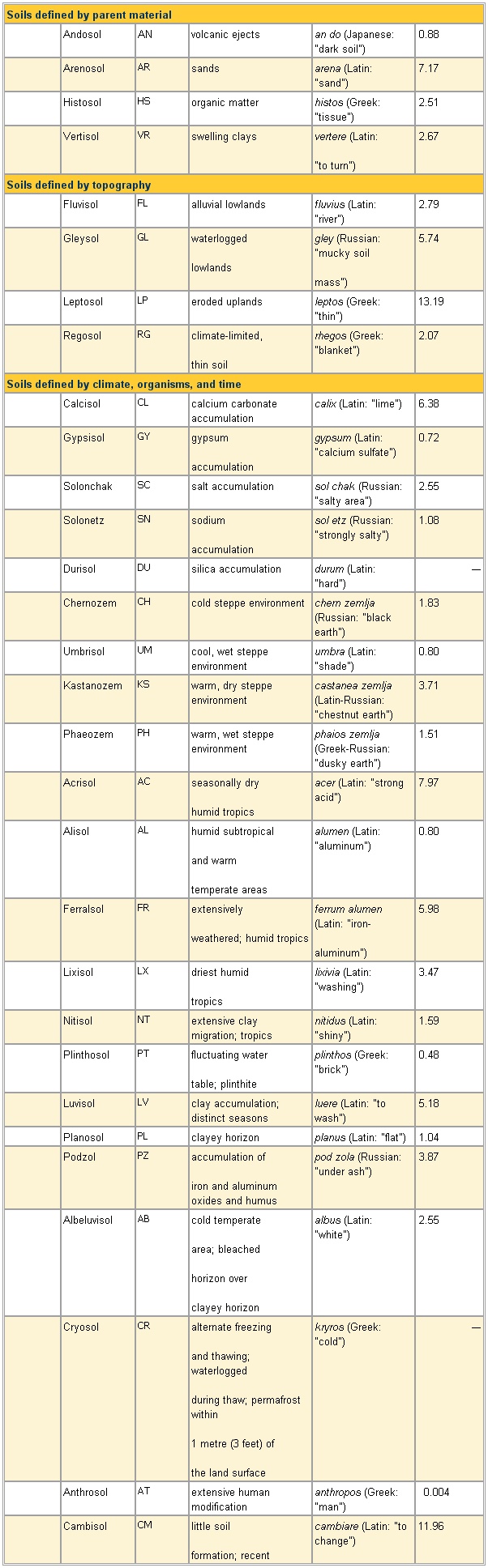
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
FAO soil classification — The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) developed a supra national classification, also called World Soil Classification, which offers useful generalizations about soils pedogenesis in relation to the interactions with… … Wikipedia
Soil classification — deals with the systematic categorization of soils based on distinguishing characteristics as well as criteria that dictate choices in use. Overview Soil classification is a dynamic subject, from the structure of the system itself, to the… … Wikipedia
soil — soil1 soilless, adj. /soyl/, n. 1. the portion of the earth s surface consisting of disintegrated rock and humus. 2. a particular kind of earth: sandy soil. 3. the ground as producing vegetation or as cultivated for its crops: fertile soil. 4. a… … Universalium
Soil science — is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to the use and… … Wikipedia
Soil survey — Soil survey, or soil mapping, is the process of classifying soil types and other soil properties in a given area and geo encoding such information. It applies the principles of soil science, and draws heavily from geomorphology, theories of soil… … Wikipedia
Soil horizon — Soil samples illustrating horizons (subsoil on right) A soil horizon is a specific layer in the land area that is parallel to the soil surface and possesses physical characteristics which differ from the layers above and beneath … Wikipedia
Soil — For other uses, see Soil (disambiguation). A represents soil; B represents laterite, a regolith; C represents saprolite, a less weathered regolith; the bottommost layer represents bedrock … Wikipedia
World Reference Base for Soil Resources — The World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) is the international standard taxonomic soil classification system endorsed by the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS). It was developed by an international collaboration coordinated by… … Wikipedia
Soil texture — is a soil property used to describe the relative proportion of different grain sizes of mineral particles in a soil. Particles are grouped according to their size into what are called soil separates. These separates are typically named clay, silt … Wikipedia
Köppen climate classification — The title of this article contains the character ö. Where it is unavailable or not desired, the name may be represented as Koppen climate classification. Updated Köppen–Geiger climate map[1] … Wikipedia
 Soils defined by parent material"to turn") 2.67Soils defined by topographyGleysol GL waterloggedmass") 5.74Regosol RG climate-limited,thin soil rhegos (Greek: "blanket") 2.07Soils defined by climate, organisms, and timeGypsisol GY gypsumSolonetz SN sodiumaccumulation sol etz (Russian: "strongly salty") 1.08Kastanozem KS warm, dry steppe environment castanea zemlja (Latin-Russian: "chestnut earth") 3.71Phaeozem PH warm, wet steppe environment phaios zemlja (Greek-Russian: "dusky earth") 1.51Acrisol AC seasonally dryhumid tropics acer (Latin: "strong acid") 7.97Alisol AL humid subtropicaland warmtemperate areas alumen (Latin: "aluminum") 0.80Ferralsol FR extensivelyweathered; humid tropics ferrum alumen (Latin: "iron-aluminum") 5.98Lixisol LX driest humidtropics lixivia (Latin: "washing") 3.47Plinthosol PT fluctuating watertable; plinthite plinthos (Greek: "brick") 0.48. Podzol PZ accumulation ofiron and aluminum oxides and humus pod zola (Russian: "under ash") 3.87Albeluvisol AB cold temperatearea; bleachedhorizon overclayey horizon albus (Latin: "white") 2.55Cryosol CR alternate freezingand thawing; waterloggedduring thaw; permafrost within1 metre (3 feet) ofthe land surface kryros (Greek: "cold") —Cambisol CM little soilformation; recent cambiare (Latin: "to change") 11.96See as table:
Soils defined by parent material"to turn") 2.67Soils defined by topographyGleysol GL waterloggedmass") 5.74Regosol RG climate-limited,thin soil rhegos (Greek: "blanket") 2.07Soils defined by climate, organisms, and timeGypsisol GY gypsumSolonetz SN sodiumaccumulation sol etz (Russian: "strongly salty") 1.08Kastanozem KS warm, dry steppe environment castanea zemlja (Latin-Russian: "chestnut earth") 3.71Phaeozem PH warm, wet steppe environment phaios zemlja (Greek-Russian: "dusky earth") 1.51Acrisol AC seasonally dryhumid tropics acer (Latin: "strong acid") 7.97Alisol AL humid subtropicaland warmtemperate areas alumen (Latin: "aluminum") 0.80Ferralsol FR extensivelyweathered; humid tropics ferrum alumen (Latin: "iron-aluminum") 5.98Lixisol LX driest humidtropics lixivia (Latin: "washing") 3.47Plinthosol PT fluctuating watertable; plinthite plinthos (Greek: "brick") 0.48. Podzol PZ accumulation ofiron and aluminum oxides and humus pod zola (Russian: "under ash") 3.87Albeluvisol AB cold temperatearea; bleachedhorizon overclayey horizon albus (Latin: "white") 2.55Cryosol CR alternate freezingand thawing; waterloggedduring thaw; permafrost within1 metre (3 feet) ofthe land surface kryros (Greek: "cold") —Cambisol CM little soilformation; recent cambiare (Latin: "to change") 11.96See as table:
