Typical density ranges for some other rock types
- Typical density ranges for some other rock types
-
Typical density ranges for some other rock types
rock type density (grams per cubic cm)
amphibolite 2.79–3.14
andesite glass 2.40–2.57
anhydrite 2.82–2.93
anorthosite 2.64–2.92
basalt glass 2.70–2.85
chalk 2.23
dolomite 2.72–2.84
dunite 2.98–3.76
eclogite 3.32–3.45
gneiss 2.59–2.84
granodiorite 2.67–2.78
limestone 1.55–2.75
marble 2.67–2.75
norite 2.72–3.02
peridotite 3.15–3.28
quartzite 2.65
rock salt 2.10–2.20
schist 2.73–3.19
shale 2.06–2.67
slate 2.72–2.84
Source: After data from R.A. Daly, G.E. Manger, and S.P. Clark, Jr. (1966); A.F. Birch (1966); F. Press (1966); and R.N. Schock, B.P. Bonner, and H. Louis (1974) in Robert S. Carmichael, ed., Handbook of Physical Properties of Rocks, vol. III, CRC Press, Inc. (1984).
See as table: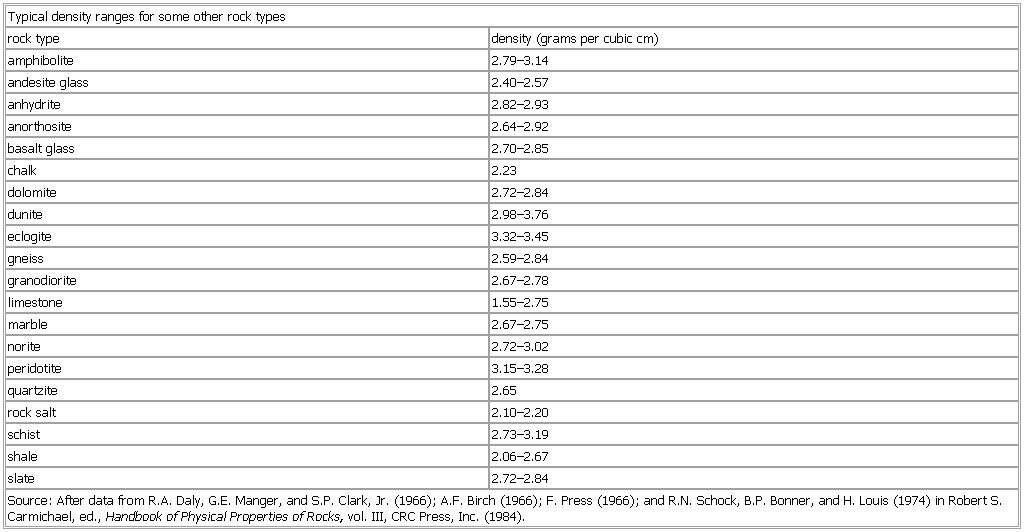
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
rock — rock1 rockless, adj. rocklike, adj. /rok/, n. 1. a large mass of stone forming a hill, cliff, promontory, or the like. 2. Geol. a. mineral matter of variable composition, consolidated or unconsolidated, assembled in masses or considerable… … Universalium
Rock — /rok/, n. a male given name. * * * I In geology, a naturally occurring and coherent aggregate of minerals. The three major classes of rock igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic are based on the processes that formed them. These three classes are… … Universalium
Rock cycle — rocks do not remain in equilibrium and are forced to change as they encounter new environments. The rock cycle is an illustration that explains how the 3 rock types are related to each other and how processes change from one type to another over… … Wikipedia
metamorphic rock — Any of a class of rocks that result from the alteration of preexisting rocks in response to changing geological conditions, including variations in temperature, pressure, and mechanical stress. The preexisting rocks may be igneous, sedimentary,… … Universalium
sedimentary rock — Rock formed at or near the Earth s surface by the accumulation and lithification of fragments of preexisting rocks or by precipitation from solution at normal surface temperatures. Sedimentary rocks can be formed only where sediments are… … Universalium
Igneous rock — Geologic provinces of the world (USGS) Shield … Wikipedia
cañada — /keuhn yah deuh, yad euh/, n. Chiefly Western U.S. 1. a dry riverbed. 2. a small, deep canyon. [1840 50; < Sp, equiv. to cañ(a) CANE + ada n. suffix] * * * Canada Introduction Canada Background: A land of vast distances and rich natural resources … Universalium
Canada — /kan euh deuh/, n. a nation in N North America: a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. 29,123,194; 3,690,410 sq. mi. (9,558,160 sq. km). Cap.: Ottawa. * * * Canada Introduction Canada Background: A land of vast distances and rich natural… … Universalium
lake — lake1 /layk/, n. 1. a body of fresh or salt water of considerable size, surrounded by land. 2. any similar body or pool of other liquid, as oil. 3. (go) jump in the lake, (used as an exclamation of dismissal or impatience.) [bef. 1000; ME lak(e) … Universalium
Lake — /layk/, n. Simon, 1866 1945, U.S. engineer and naval architect. * * * I Relatively large body of slow moving or standing water that occupies an inland basin. Lakes are most abundant in high northern latitudes and in mountain regions, particularly … Universalium

