Carbon sequestration — is the capture of carbon dioxide (CO2) and may refer specifically to: The process of removing carbon from the atmosphere and depositing it in a reservoir. [1] When carried out deliberately, this may also be referred to as carbon dioxide removal,… … Wikipedia
Carbon negative — is any process that removes carbon, in any form, from the atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere in such a way that it cannot return. Carbon negative processes are the opposite of carbon positive processes. Carbon dioxide sinks and carbon… … Wikipedia
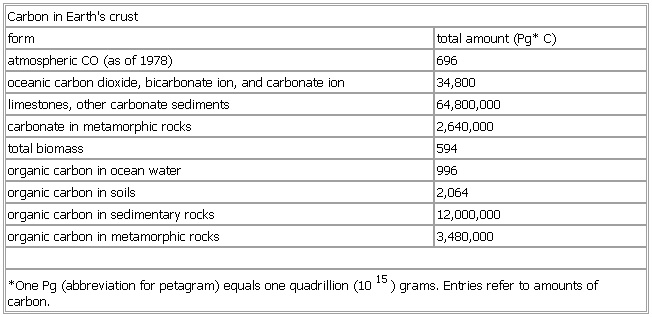
Earth Sciences — ▪ 2009 Introduction Geology and Geochemistry The theme of the 33rd International Geological Congress, which was held in Norway in August 2008, was “Earth System Science: Foundation for Sustainable Development.” It was attended by nearly… … Universalium
earth — /errth/, n. 1. (often cap.) the planet third in order from the sun, having an equatorial diameter of 7926 mi. (12,755 km) and a polar diameter of 7900 mi. (12,714 km), a mean distance from the sun of 92.9 million mi. (149.6 million km), and a… … Universalium
Earth — This article is about the planet. For other uses, see Earth (disambiguation). Earth … Wikipedia
carbon group element — ▪ chemical elements Introduction any of the five chemical elements that make up Group 14 (IVa) of the periodic table namely, carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), and lead ( … Universalium
carbon cycle — 1. Ecol. the circulation of carbon atoms in the biosphere as a result of photosynthetic conversion of carbon dioxide into complex organic compounds by plants, which are consumed by other organisms: the carbon returns to the atmosphere in the form … Universalium
Carbon group — The carbon group is group 14 (IUPAC style) in the periodic table. Once also known as the tetrels (from Latin tetra , four), stemming from the earlier naming convention of this group as Group IVA. The group consists of carbon (C), silicon (Si),… … Wikipedia
carbon — carbonless, adj. /kahr beuhn/, n. 1. Chem. a widely distributed element that forms organic compounds in combination with hydrogen, oxygen, etc., and that occurs in a pure state as diamond and graphite, and in an impure state as charcoal. Symbol:… … Universalium
Earth battery — An Earth battery is composed of a pair of electrodes made of two dissimilar metals, such as iron and copper, which are buried in the soil or immersed in the sea. A device that is placed in water is labeled a sea battery . It can act as a receiver … Wikipedia