- Drugs acting on cholinergic and adrenergic receptors
-
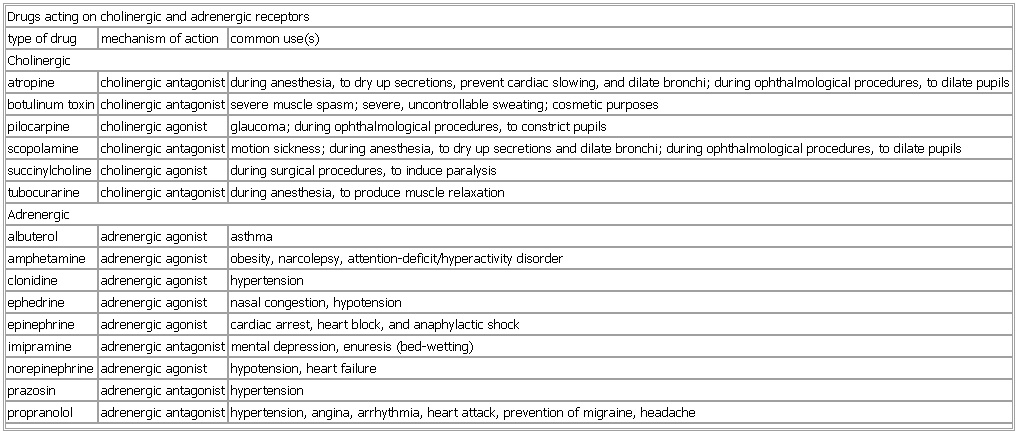
▪ TableDrugs acting on cholinergic and adrenergic receptorstype of drug mechanism of action common use(s)Cholinergicatropine cholinergic antagonist during anesthesia, to dry up secretions, prevent cardiac slowing, and dilate bronchi; during ophthalmological procedures, to dilate pupilsbotulinum toxin cholinergic antagonist severe muscle spasm; severe, uncontrollable sweating; cosmetic purposespilocarpine cholinergic agonist glaucoma; during ophthalmological procedures, to constrict pupilsscopolamine cholinergic antagonist motion sickness; during anesthesia, to dry up secretions and dilate bronchi; during ophthalmological procedures, to dilate pupilssuccinylcholine cholinergic agonist during surgical procedures, to induce paralysistubocurarine cholinergic antagonist during anesthesia, to produce muscle relaxationAdrenergicalbuterol adrenergic agonist asthmaamphetamine adrenergic agonist obesity, narcolepsy, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorderclonidine adrenergic agonist hypertensionephedrine adrenergic agonist nasal congestion, hypotensionepinephrine adrenergic agonist cardiac arrest, heart block, and anaphylactic shocknorepinephrine adrenergic agonist hypotension, heart failureprazosin adrenergic antagonist hypertensionpropranolol adrenergic antagonist hypertension, angina, arrhythmia, heart attack, prevention of migraine, headacheSee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
