- Space stations, from 1971
-
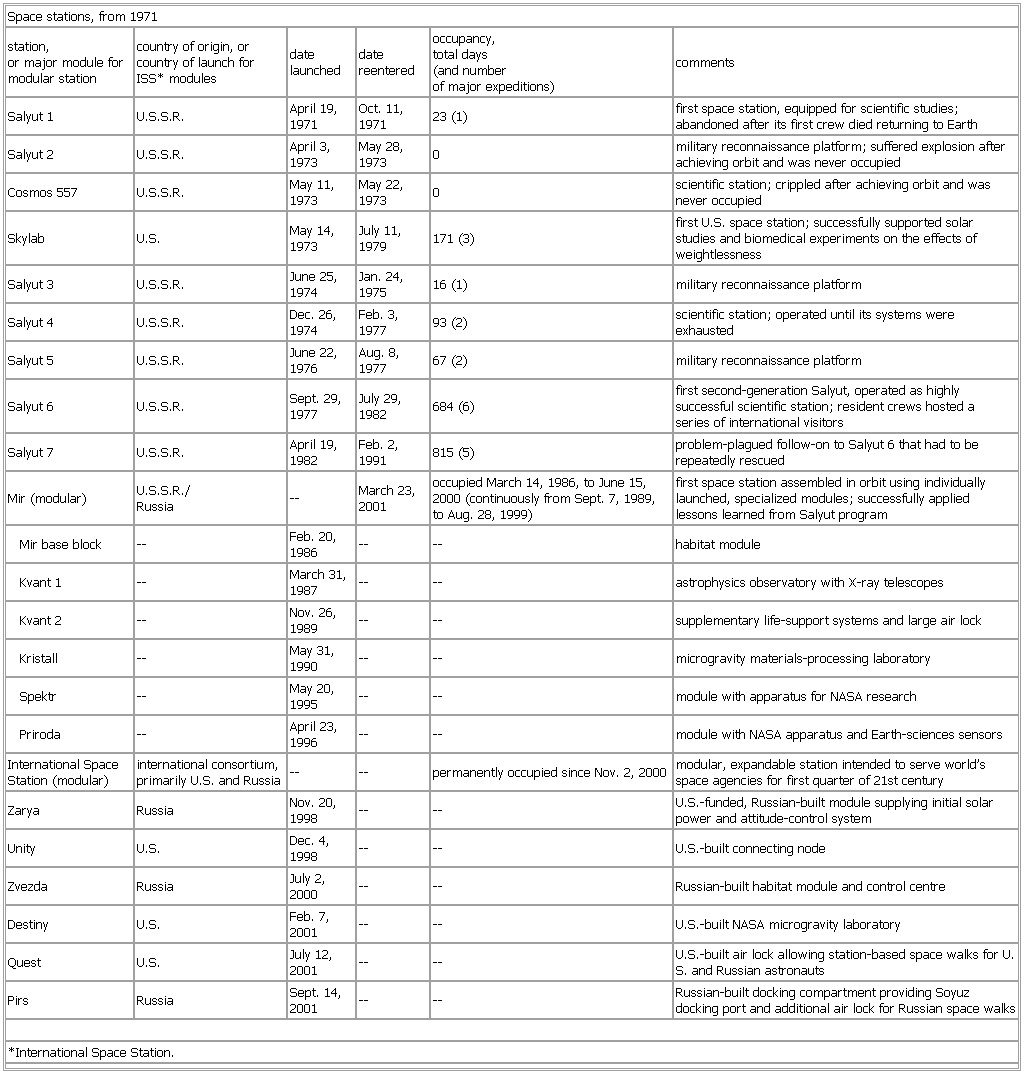
▪ TableSpace stations, from 1971station,or major module for modular station country of origin, or country of launch forISS* modules date launched date reentered occupancy,total days(and numberof major expeditions) commentsSalyut 1 U.S.S.R. April 19, 1971 Oct. 11, 1971 23 (1) first space station, equipped for scientific studies; abandoned after its first crew died returning to EarthSalyut 2 U.S.S.R. April 3, 1973 May 28, 1973 0 military reconnaissance platform; suffered explosion after achieving orbit and was never occupiedCosmos 557 U.S.S.R. May 11, 1973 May 22, 1973 0 scientific station; crippled after achieving orbit and was never occupiedSkylab U.S. May 14, 1973 July 11, 1979 171 (3) first U.S. space station; successfully supported solar studies and biomedical experiments on the effects of weightlessnessSalyut 3 U.S.S.R. June 25, 1974 Jan. 24, 1975 16 (1) military reconnaissance platformSalyut 4 U.S.S.R. Dec. 26, 1974 Feb. 3, 1977 93 (2) scientific station; operated until its systems were exhaustedSalyut 5 U.S.S.R. June 22, 1976 Aug. 8, 1977 67 (2) military reconnaissance platformSalyut 6 U.S.S.R. Sept. 29, 1977 July 29, 1982 684 (6) first second-generation Salyut, operated as highly successful scientific station; resident crews hosted a series of international visitorsSalyut 7 U.S.S.R. April 19, 1982 Feb. 2, 1991 815 (5) problem-plagued follow-on to Salyut 6 that had to be repeatedly rescuedRussia — March 23, 2001 occupied March 14, 1986, to June 15, 2000 (continuously from Sept. 7, 1989, to Aug. 28, 1999) first space station assembled in orbit using individually launched, specialized modules; successfully applied lessons learned from Salyut programMir base block — Feb. 20, 1986 — — habitat moduleKvant 1 — March 31, 1987 — — astrophysics observatory with X-ray telescopesKvant 2 — Nov. 26, 1989 — — supplementary life-support systems and large air lockKristall — May 31, 1990 — — microgravity materials-processing laboratorySpektr — May 20, 1995 — — module with apparatus for NASA researchPriroda — April 23, 1996 — — module with NASA apparatus and Earth-sciences sensorsInternational Space Station (modular) international consortium, primarily U.S. and Russia — — permanently occupied since Nov. 2, 2000 modular, expandable station intended to serve world’s space agencies for first quarter of 21st centuryZarya Russia Nov. 20, 1998 — — U.S.-funded, Russian-built module supplying initial solar power and attitude-control systemUnity U.S. Dec. 4, 1998 — — U.S.-built connecting nodeZvezda Russia July 2, 2000 — — Russian-built habitat module and control centreDestiny U.S. Feb. 7, 2001 — — U.S.-built NASA microgravity laboratoryQuest U.S. July 12, 2001 — — U.S.-built air lock allowing station-based space walks for U.S. and Russian astronautsPirs Russia Sept. 14, 2001 — — Russian-built docking compartment providing Soyuz docking port and additional air lock for Russian space walks*International Space Station.See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
