- Notable early nuclear reactors
-
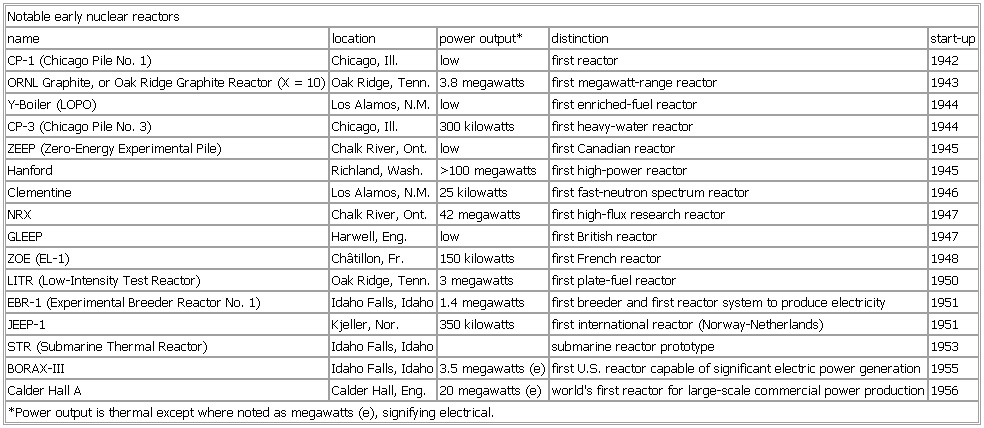
▪ TableNotable early nuclear reactorsname location power output* distinction start-upCP-1 (Chicago Pile No. 1) Chicago, Ill. low first reactor 1942ORNL Graphite, or Oak Ridge Graphite Reactor (X = 10) Oak Ridge, Tenn. 3.8 megawatts first megawatt-range reactor 1943Y-Boiler (LOPO) Los Alamos, N.M. low first enriched-fuel reactor 1944CP-3 (Chicago Pile No. 3) Chicago, Ill. 300 kilowatts first heavy-water reactor 1944ZEEP (Zero-Energy Experimental Pile) Chalk River, Ont. low first Canadian reactor 1945Hanford Richland, Wash. >100 megawatts first high-power reactor 1945Clementine Los Alamos, N.M. 25 kilowatts first fast-neutron spectrum reactor 1946NRX Chalk River, Ont. 42 megawatts first high-flux research reactor 1947GLEEP Harwell, Eng. low first British reactor 1947ZOE (EL-1) Châtillon, Fr. 150 kilowatts first French reactor 1948LITR (Low-Intensity Test Reactor) Oak Ridge, Tenn. 3 megawatts first plate-fuel reactor 1950EBR-1 (Experimental Breeder Reactor No. 1) Idaho Falls, Idaho 1.4 megawatts first breeder and first reactor system to produce electricity 1951JEEP-1 Kjeller, Nor. 350 kilowatts first international reactor (Norway-Netherlands) 1951STR (Submarine Thermal Reactor) Idaho Falls, Idaho submarine reactor prototype 1953BORAX-III Idaho Falls, Idaho 3.5 megawatts (e) first U.S. reactor capable of significant electric power generation 1955Calder Hall A Calder Hall, Eng. 20 megawatts (e) world's first reactor for large-scale commercial power production 1956*Power output is thermal except where noted as megawatts (e), signifying electrical.See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
