- Earth Perihelion and Aphelion, 2009
-
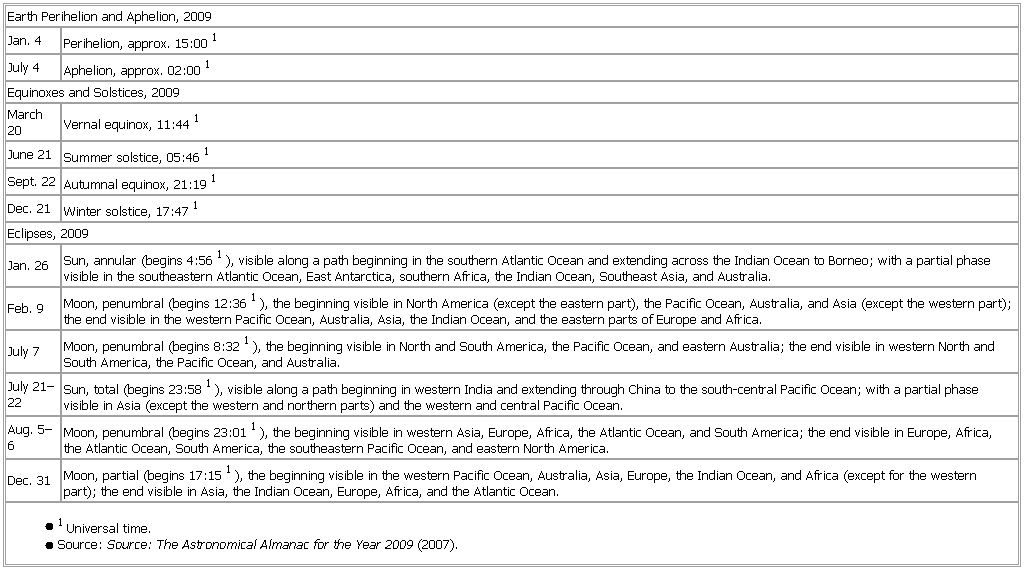
▪ TableEarth Perihelion and Aphelion, 2009Jan. 4 Perihelion, approx. 15:001July 4 Aphelion, approx. 02:001Equinoxes and Solstices, 2009March 20 Vernal equinox, 11:441June 21 Summer solstice, 05:461Sept. 22 Autumnal equinox, 21:191Dec. 21 Winter solstice, 17:471Eclipses, 2009Jan. 26 Sun, annular (begins 4:561), visible along a path beginning in the southern Atlantic Ocean and extending across the Indian Ocean to Borneo; with a partial phase visible in the southeastern Atlantic Ocean, East Antarctica, southern Africa, the Indian Ocean, Southeast Asia, and Australia.Feb. 9 Moon, penumbral (begins 12:361), the beginning visible in North America (except the eastern part), the Pacific Ocean, Australia, and Asia (except the western part); the end visible in the western Pacific Ocean, Australia, Asia, the Indian Ocean, and the eastern parts of Europe and Africa.July 7 Moon, penumbral (begins 8:321), the beginning visible in North and South America, the Pacific Ocean, and eastern Australia; the end visible in western North and South America, the Pacific Ocean, and Australia.July 21–22 Sun, total (begins 23:581), visible along a path beginning in western India and extending through China to the south-central Pacific Ocean; with a partial phase visible in Asia (except the western and northern parts) and the western and central Pacific Ocean.Aug. 5–6 Moon, penumbral (begins 23:011), the beginning visible in western Asia, Europe, Africa, the Atlantic Ocean, and South America; the end visible in Europe, Africa, the Atlantic Ocean, South America, the southeastern Pacific Ocean, and eastern North America.Dec. 31 Moon, partial (begins 17:151), the beginning visible in the western Pacific Ocean, Australia, Asia, Europe, the Indian Ocean, and Africa (except for the western part); the end visible in Asia, the Indian Ocean, Europe, Africa, and the Atlantic Ocean.● 1Universal time.See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
