Physical properties of unbranched alkanes
- Physical properties of unbranched alkanes
-
Physical properties of unbranched alkanes
name formula boiling
point (°C) melting
point (°C)
methane CH4 −164 −182.5
ethane CH3CH3 −88.6 −183.3
propane CH3CH2CH3 −42 −189.7
butane CH
3(
CH2)
2CH
3 −0.5 −138.35
pentane CH
3(
CH2)
3CH
3 b;36.1 −129.7
hexane CH
3(
CH2)
4CH
3 b;68.9 −95.0
heptane CH
3(
CH2)
5CH
3 b;98.4 −90.6
octane CH
3(
CH2)
6CH
3 b;125.6 −56.8
nonane CH
3(
CH2)
7CH
3 b;150.8 −51.0
decane CH
3(
CH2)
8CH
3 b;174.1 −29.7
pentadecane CH
3(
CH2)
13CH
3 b;270 b;10
octadecane CH
3(
CH2)
16CH
3 b;316.1 b;28.2
icosane CH
3(
CH2)
18CH
3 b;343 b;36.8
triacontane CH
3(
CH2)
28CH
3 b;449.7 b;65.8
tetracontane CH
3(
CH2)
38CH
3 — b;81
pentacontane CH
3(
CH2)
48CH
3 — b;92
See as table: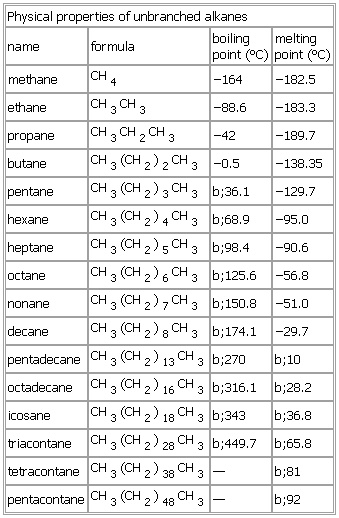
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
hydrocarbon — hydrocarbonaceous, adj. /huy dreuh kahr beuhn, huy dreuh kahr /, n. any of a class of compounds containing only hydrogen and carbon, as an alkane, methane, CH4, an alkene, ethylene, C2H4, an alkyne, acetylene, C2H2, or an aromatic compound,… … Universalium
Alkane — Not to be confused with Alkene or Alkyne. Chemical structure of methane, the simplest alkane Alkanes (also known as paraffins or saturated hydrocarbons) are chemical compounds that consist only of hydrogen and carbon atoms and are bonded… … Wikipedia
Pentane — n Pentane … Wikipedia
Hexane — n Hexane … Wikipedia
Nylon — For other uses, see Nylon (disambiguation). Nylon Density 1.15 g/cm3 Electrical conductivity (σ) 10 … Wikipedia

