Names of fundamental structures most often used in steroid nomenclature
- Names of fundamental structures most often used in steroid nomenclature
-
Names of fundamental structures most often used in steroid nomenclature
carbon atoms present (as numbered in structure 6) naturally occurring
general
classes examples shown in text
gonane 1–17 none gonane* (1)
estrane 1–18 estrogens estradiol (17f)
androstane 1–19 androgens androstane* (2–5); testosterone (17e); androstanedione (17c)
pregnane 1–21 gestogens and adrenal steroids progesterone (17a); cortisol (17b); aldosterone (17d); batrachotoxin (14)
cholane 1–24 bile acids cholic acid (10a); sodium sodium glycocholate (10b)
cholestane 1–27 sterols cholesterol (16d); scymnol (11a)
ergostane 1–28 sterols ergosterol (8); cyasterone (22)
stigmastane 1–29 sterols stigmasterol (7); antheridiol (12)
lanostane 1–27; 30–32 trimethyl sterols lanosterol (16c);
22,25-oxidoholothurinogenin (13)
cardanolide 1–23 cardiac glycosides digitoxigenin (23)
bufanolide 1–24 toad poisons bufotoxin (24)
spirostan 1–27 sapogenins dioscin (25)
*Gonane and androstane themselves do not occur in nature.
See as table: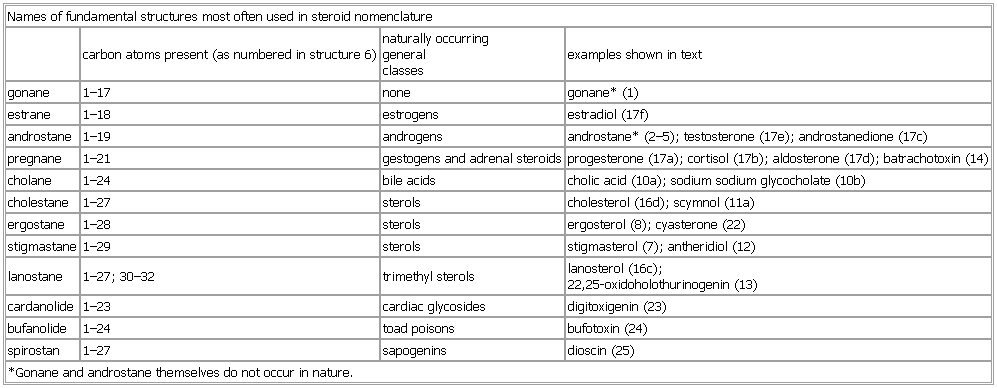
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
steroid — /stear oyd, ster /, Biochem. n. 1. any of a large group of fat soluble organic compounds, as the sterols, bile acids, and sex hormones, most of which have specific physiological action. adj. 2. Also, steroidal /sti royd l, ste /. pertaining to or … Universalium
heterocyclic compound — Any of a class of organic compounds whose molecules contain one or more rings of atoms with at least one atom (the heteroatom) being an element other than carbon, most frequently oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. As in regular cyclic hydrocarbons,… … Universalium
Life Sciences — ▪ 2009 Introduction Zoology In 2008 several zoological studies provided new insights into how species life history traits (such as the timing of reproduction or the length of life of adult individuals) are derived in part as responses to… … Universalium
chemistry — /kem euh stree/, n., pl. chemistries. 1. the science that deals with the composition and properties of substances and various elementary forms of matter. Cf. element (def. 2). 2. chemical properties, reactions, phenomena, etc.: the chemistry of… … Universalium

