Some typical values of elastic constants and properties
- Some typical values of elastic constants and properties
-
Some typical values of elastic constants and properties
elastic constants (at room temperature and pressure)
material Young's modulus
(in 106 bars) shear modulus
(in 106 bars)
ice 0.1 0.03
shale 0.2–0.3 0.15
limestone 0.4–0.7 0.22–0.26
granite 0.3–0.6 0.2
basalt 0.7–0.9 0.3
steel 2.1 0.83
material temperature
(degrees Celsius) coefficient of viscosity
(poises)
lava (Mount Vesuvius) 1,100
1,400 28,300
250
lava (Oshima,
Japan) 1,038
1,125 230,000
5,600
andesite lava 1,400 150–1,500
material compressive strength
(at room temperature and pressure, in kilobars)
shale 0.8–1.8
sandstone 0.5–2
limestone 1–2
granite 1.7–2.5
basalt 1–3.4
See as table: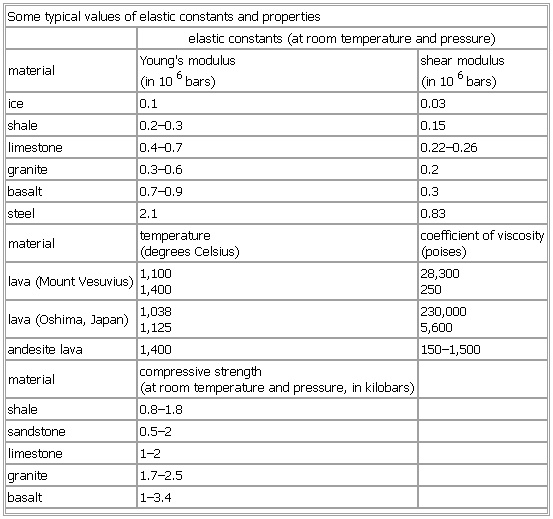
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
rock — rock1 rockless, adj. rocklike, adj. /rok/, n. 1. a large mass of stone forming a hill, cliff, promontory, or the like. 2. Geol. a. mineral matter of variable composition, consolidated or unconsolidated, assembled in masses or considerable… … Universalium
Rock — /rok/, n. a male given name. * * * I In geology, a naturally occurring and coherent aggregate of minerals. The three major classes of rock igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic are based on the processes that formed them. These three classes are… … Universalium
Crystal oscillator — A miniature 4 MHz quartz crystal enclosed in a hermetically sealed HC 49/US package, used as the resonator in a crystal oscillator. A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal … Wikipedia
solids, mechanics of — ▪ physics Introduction science concerned with the stressing (stress), deformation (deformation and flow), and failure of solid materials and structures. What, then, is a solid? Any material, fluid or solid, can support normal forces.… … Universalium
analysis — /euh nal euh sis/, n., pl. analyses / seez /. 1. the separating of any material or abstract entity into its constituent elements (opposed to synthesis). 2. this process as a method of studying the nature of something or of determining its… … Universalium
gas — gasless, adj. /gas/, n., pl. gases, v., gassed, gassing. n. 1. Physics. a substance possessing perfect molecular mobility and the property of indefinite expansion, as opposed to a solid or liquid. 2. any such fluid or mixture of fluids. 3. any… … Universalium
mathematics — /math euh mat iks/, n. 1. (used with a sing. v.) the systematic treatment of magnitude, relationships between figures and forms, and relations between quantities expressed symbolically. 2. (used with a sing. or pl. v.) mathematical procedures,… … Universalium
electricity — /i lek tris i tee, ee lek /, n. 1. See electric charge. 2. See electric current. 3. the science dealing with electric charges and currents. 4. a state or feeling of excitement, anticipation, tension, etc. [1640 50; ELECTRIC + ITY] * * *… … Universalium
rare-earth element — /rair errth /, Chem. any of a group of closely related metallic elements, comprising the lanthanides, scandium, and yttrium, that are chemically similar by virtue of having the same number of valence electrons. Also called rare earth metal. [1955 … Universalium
Liquid crystal — Schlieren texture of liquid crystal nematic phase Liquid crystals (LCs) are a state of matter that have properties between those of a conventional liquid and those of a solid crystal.[1] For instance, an LC may flow like a liquid, but its… … Wikipedia

