Estimate of excess volatiles
- Estimate of excess volatiles
-
Estimate of "excess volatiles"
(units of 1020 grams)
water 16,600
total carbon as carbon dioxide 910
sulfur 22
nitrogen 42
chlorine 300
hydrogen 10
boron, bromine, argon, fluorine, etc. 4
Source: W.W. Rubey (1951).
See as table: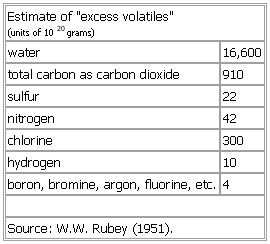
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Estimate of excess volatiles 1 — ▪ Table Estimate of excess volatiles (units of 1020 grams) water 16,660 total carbon as carbon dioxide 2,500 chlorine 300 nitrogen 49 sulfur 44 boron, bromine, argon, fluorine, etc. 4 Source: J.C.G. Walker, Evolution of the Atmosphere (1977).… … Universalium
hydrosphere — /huy dreuh sfear /, n. the water on or surrounding the surface of the globe, including the water of the oceans and the water in the atmosphere. [1885 90; HYDRO 1 + SPHERE] * * * Discontinuous layer of water at or near the Earth s surface. It… … Universalium
chemical element — Introduction also called element, any substance that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by ordinary chemical processes. Elements are the fundamental materials of which all matter is composed. This article considers the… … Universalium
sedimentary rock — Rock formed at or near the Earth s surface by the accumulation and lithification of fragments of preexisting rocks or by precipitation from solution at normal surface temperatures. Sedimentary rocks can be formed only where sediments are… … Universalium
Abiogenesis — Primordial soup redirects here. For the board game, see Primordial Soup (board game). Origin of life redirects here. For views on the origins of life outside the natural sciences, see Creation myth. Pre Cambrian stromatolites in the Siyeh… … Wikipedia
rock — rock1 rockless, adj. rocklike, adj. /rok/, n. 1. a large mass of stone forming a hill, cliff, promontory, or the like. 2. Geol. a. mineral matter of variable composition, consolidated or unconsolidated, assembled in masses or considerable… … Universalium
Rock — /rok/, n. a male given name. * * * I In geology, a naturally occurring and coherent aggregate of minerals. The three major classes of rock igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic are based on the processes that formed them. These three classes are… … Universalium
Earth, geologic history of — Introduction evolution of the continents, oceans, atmosphere, and biosphere. The layers of rock at the Earth s surface contain evidence of the evolutionary processes undergone by these components of the terrestrial environment during the… … Universalium

