Average net primary production of the Earth's major habitats
- Average net primary production of the Earth's major habitats
-
Average net primary production of the Earth's major habitats
habitat net primary
production
(gram per
square metre
per year)
Forests
tropical 1,800
temperate 1,250
boreal 800
Other terrestrial habitats
swamp and marsh 2,500
savanna 700
cultivated land 650
shrubland 600
desert scrub 70
temperate grassland 500
tundra and alpine 140
Aquatic habitats
algal beds and reefs 2,000
estuaries 1,800
lakes and streams 500
continental shelf 360
open ocean 125
Source: Adapted from Robert E. Ricklefs,
Ecology, 3rd edition (1990),
by W.H. Freeman and Company, used with permission.
See as table: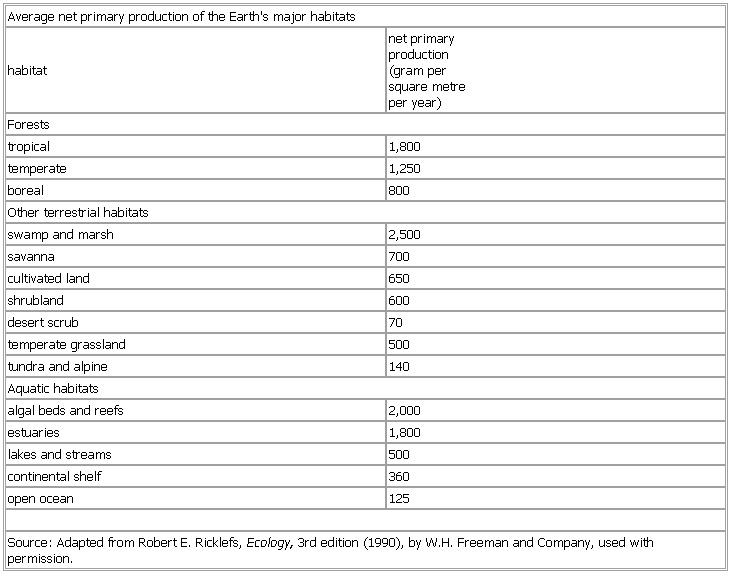
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Primary production — For other uses, see Primary production (economics). Global oceanic and terrestrial photoautotroph abundance, from September 1997 to August 2000. As an estimate of autotroph biomass, it is only a rough indicator of primary production potential,… … Wikipedia
biosphere — biospheric /buy euh sfer ik/, adj. /buy euh sfear /, n. 1. the part of the earth s crust, waters, and atmosphere that supports life. 2. the ecosystem comprising the entire earth and the living organisms that inhabit it. [1895 1900; < G Biosphäre; … Universalium
Marine habitats — Coral reefs provide marine habitats for tube sponges, which in turn become marine habitats for fishes Littoral zone … Wikipedia
Biome — The planet Earth Biomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms,[1] and are of … Wikipedia
Kobuk River — The Kobuk River is approximately convert|280|mi|km|0|lk=on long, located in the Arctic region of northwestern Alaska in the United States. [USGS Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). [http://geonames.usgs.gov/pls/gnispublic/f?p=gnispq:3:::NO… … Wikipedia
soil — soil1 soilless, adj. /soyl/, n. 1. the portion of the earth s surface consisting of disintegrated rock and humus. 2. a particular kind of earth: sandy soil. 3. the ground as producing vegetation or as cultivated for its crops: fertile soil. 4. a… … Universalium
Wetland — For other uses, see Wetland (disambiguation). The Florida Everglades massive wetland system in the United States saw 1.7 billion gallons of fresh water flushed from it daily and pumped into the ocean following one of the most successive water… … Wikipedia
Aquatic ecosystem — An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem located in water bodies. Communities of organisms that are dependent on each other and on their environment live in aquatic ecosystems. The two main types of aquatic ecosystems are marine ecosystems and… … Wikipedia
Paleolithic — The Paleolithic This box: view · talk · edit ↑ before Homo (Plioc … Wikipedia
Severn Barrage — The Severn Barrage is the name of a number of ideas for building a barrage from the English coast to the Welsh coast over the Severn tidal estuary. Ideas for damming or barraging the Severn estuary (and Bristol Channel) have existed since the… … Wikipedia

