- Some properties of the boron group elements
-
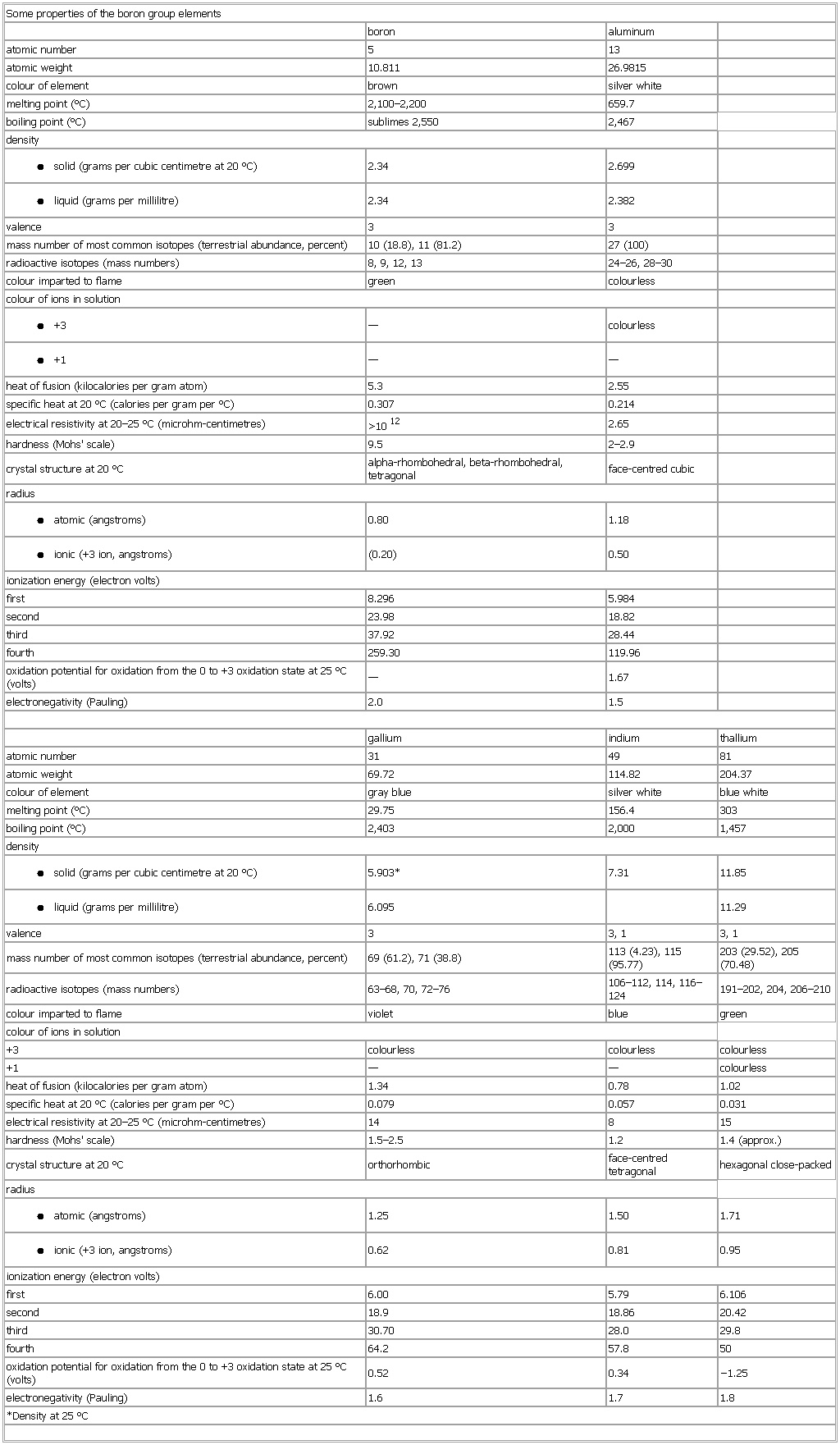
▪ TableSome properties of the boron group elementsboron aluminumatomic number 5 13atomic weight 10.811 26.9815colour of element brown silver whitemelting point (°C) 2,100–2,200 659.7boiling point (°C) sublimes 2,550 2,467density● solid (grams per cubic centimetre at 20 °C)2.34 2.699● liquid (grams per millilitre)2.34 2.382valence 3 3mass number of most common isotopes (terrestrial abundance, percent) 10 (18.8), 11 (81.2) 27 (100)radioactive isotopes (mass numbers) 8, 9, 12, 13 24–26, 28–30colour imparted to flame green colourlesscolour of ions in solution● +3— colourless● +1— —heat of fusion (kilocalories per gram atom) 5.3 2.55specific heat at 20 °C (calories per gram per °C) 0.307 0.214electrical resistivity at 20–25 °C (microhm-centimetres) >1012 2.65hardness (Mohs' scale) 9.5 2–2.9crystal structure at 20 °C alpha-rhombohedral, beta-rhombohedral, tetragonal face-centred cubicradius● atomic (angstroms)0.80 1.18● ionic (+3 ion, angstroms)(0.20) 0.50ionization energy (electron volts)first 8.296 5.984second 23.98 18.82third 37.92 28.44fourth 259.30 119.96oxidation potential for oxidation from the 0 to +3 oxidation state at 25 °C (volts) — 1.67electronegativity (Pauling) 2.0 1.5gallium indium thalliumatomic number 31 49 81atomic weight 69.72 114.82 204.37colour of element gray blue silver white blue whitemelting point (°C) 29.75 156.4 303boiling point (°C) 2,403 2,000 1,457density● solid (grams per cubic centimetre at 20 °C)5.903* 7.31 11.85● liquid (grams per millilitre)6.095 11.29valence 3 3, 1 3, 1mass number of most common isotopes (terrestrial abundance, percent) 69 (61.2), 71 (38.8) 113 (4.23), 115 (95.77) 203 (29.52), 205 (70.48)radioactive isotopes (mass numbers) 63–68, 70, 72–76 106–112, 114, 116–124 191–202, 204, 206–210colour imparted to flame violet blue greencolour of ions in solution+3 colourless colourless colourless+1 — — colourlessheat of fusion (kilocalories per gram atom) 1.34 0.78 1.02specific heat at 20 °C (calories per gram per °C) 0.079 0.057 0.031electrical resistivity at 20–25 °C (microhm-centimetres) 14 8 15hardness (Mohs' scale) 1.5–2.5 1.2 1.4 (approx.)crystal structure at 20 °C orthorhombic face-centred tetragonal hexagonal close-packedradius● atomic (angstroms)1.25 1.50 1.71● ionic (+3 ion, angstroms)0.62 0.81 0.95ionization energy (electron volts)first 6.00 5.79 6.106second 18.9 18.86 20.42third 30.70 28.0 29.8fourth 64.2 57.8 50oxidation potential for oxidation from the 0 to +3 oxidation state at 25 °C (volts) 0.52 0.34 −1.25electronegativity (Pauling) 1.6 1.7 1.8*Density at 25 °CSee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
